Article contents
Exit Wave Reconstruction of Interfaces Between Zno Films and ScalmgO4 Substrates
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 July 2020
Abstract
Epitaxial ZnO thin films were produced on basal plane ScAlMgO4 (SAM) by chemical solution deposition (CSD) (fig. 1). ZnO crystallizes in the wurtzite structure and ScAlMgO4 is isostructural to YbFe2O4, a layered structure shown in fig. 2. The crystallographic orientation relationship was observed by XRD using θ-2θ scans and off-axis φ scans to be (0001)zno ∥ (0001)SAM and 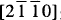 zno ∥
zno ∥ 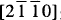 SAM. The lattice mismatch between film and substrate is 0,09%.
SAM. The lattice mismatch between film and substrate is 0,09%.
For TEM observations in cross-sectional geometry two substrates were glued together with the epitaxial film surfaces. Electron transparent specimens were produced by standard methods of mechanical thinning and ion beam etching. The HRTEM investigations were performed on a Philips CM300 FEG electron microscope with Ultra-Twin lens operated at 300 kV. After correction of axial coma and two-fold astigmatism images were recorded on a slow-scan lk × lk CCD camera with a sampling of 0.0193 nm/pixel.
- Type
- Quantitative Transmission Electron Microscopy of Interfaces (Organized by M. Rüehle, Y. Zhu and U. Dahmen)
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Microscopy Society of America 2001
References
- 1
- Cited by


