Published online by Cambridge University Press: 11 February 2016
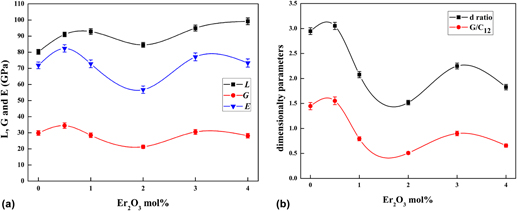
Glasses doped with rare earth elements (lanthanide series) are the most popular materials used in upconversion devices. The main aspect to develop these devices is to find suitable host materials for rare earth ions. The host material should have a high transmission of the upconverted photons, high thermal stability, good mechanical properties, low price, and easy to manufacture and shaping. Present work is concerned with studying the mechanical and structural properties for the oxide glass system doped with rare earth metal (erbium oxide, Er2O3). Ultrasonic pulse-echo technique is used to measure the sound velocities in the glass system (30%B2O3·30%Bi2O3·20%Li2O·10%BaO·10%Pb3O4·xEr2O3), (x = 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4) mol%. Ultrasound velocities (longitudinal and shear) are measured as a function of the Er2O3 content at a frequency of 4 MHz for longitudinal wave and 2 MHz for the shear wave at a temperature of 300 K. The elastic moduli and some physical parameters, such as Debye temperature, coordination number, and compressibility, were evaluated. Furthermore, the dimensionality of the glass network has been calculated in terms of the d ratio which equals G/B ratio. These parameters beside the x-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, and Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) measurements throw more light on the structure of the glass system. The measurements in this study exhibit remarkable anomalous changes in the network structure of the investigated glass doped with Er2O3.