Article contents
Vortex-induced vibration of a two degree-of-freedom flexibly mounted circular cylinder in the crossflow direction
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 November 2022
Abstract
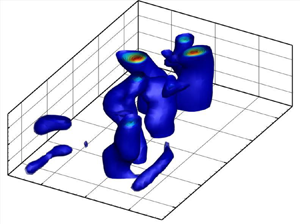
Vortex-induced vibration (VIV) of a two degree-of-freedom (DOF) circular cylinder, placed in the test section of a recirculating water tunnel and free to oscillate in its first two vibrational modes in the crossflow direction, is studied experimentally. The dynamic response of the cylinder is studied for a reduced velocity range of  $U^*=4\unicode{x2013}30$ for eigenfrequency ratios in the range of 1.3–3.0. For the two DOF system, while the onset of the VIV response followed a similar lock-in region as those observed for a classical VIV response of a single DOF system, by increasing the reduced velocity a secondary lock-in region was observed over which the oscillations of the cylinder were locked into the system's second mode. In addition, there existed an intermediate range of reduced velocity over which the VIV response consisted of oscillations at a combination of the first two natural modes of the system. As the eigenfrequency ratio between the first two modes increased, the secondary lock-in range was extended to higher reduced velocities and the reduced velocity range over which multi-modal oscillations were observed was decreased. A full map of vortex dynamics in the wake of the cylinder was developed qualitatively and quantitatively using hydrogen bubble flow visualization and time-resolved volumetric particle tracking velocimetry techniques, respectively. A Q-criterion analysis revealed the existence of highly three-dimensional vortex structures in the wake of the cylinder. The spatiotemporal mode analysis using the proper orthogonal decomposition technique revealed strong coupling between the vortex shedding modes in the wake of the cylinder and the structural vibration modes.
$U^*=4\unicode{x2013}30$ for eigenfrequency ratios in the range of 1.3–3.0. For the two DOF system, while the onset of the VIV response followed a similar lock-in region as those observed for a classical VIV response of a single DOF system, by increasing the reduced velocity a secondary lock-in region was observed over which the oscillations of the cylinder were locked into the system's second mode. In addition, there existed an intermediate range of reduced velocity over which the VIV response consisted of oscillations at a combination of the first two natural modes of the system. As the eigenfrequency ratio between the first two modes increased, the secondary lock-in range was extended to higher reduced velocities and the reduced velocity range over which multi-modal oscillations were observed was decreased. A full map of vortex dynamics in the wake of the cylinder was developed qualitatively and quantitatively using hydrogen bubble flow visualization and time-resolved volumetric particle tracking velocimetry techniques, respectively. A Q-criterion analysis revealed the existence of highly three-dimensional vortex structures in the wake of the cylinder. The spatiotemporal mode analysis using the proper orthogonal decomposition technique revealed strong coupling between the vortex shedding modes in the wake of the cylinder and the structural vibration modes.
JFM classification
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally to this work.
References
REFERENCES
Mousavisani et al. supplementary movie 1
Mousavisani et al. supplementary movie 2
- 9
- Cited by



