Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Jambon-Puillet, Etienne
Shahidzadeh, Noushine
and
Bonn, Daniel
2018.
Singular sublimation of ice and snow crystals.
Nature Communications,
Vol. 9,
Issue. 1,
Liu, Jie
Huang, Kun
Liu, Wenqian
Zhang, Kaiqiang
Wu, Xiaohong
Zhao, Zhenmin
and
Liu, Huizhou
2019.
Wettability and spreading behavior of organic extractant and its effect on formation of gas bubble supported organic liquid membrane for large-phase-ratio extraction.
Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification,
Vol. 144,
Issue. ,
p.
107657.
Zitz, S.
Scagliarini, A.
Maddu, S.
Darhuber, A. A.
and
Harting, J.
2019.
Lattice Boltzmann method for thin-liquid-film hydrodynamics.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 100,
Issue. 3,
Rednikov, A. Y.
and
Colinet, P.
2019.
Contact-line singularities resolved exclusively by the Kelvin effect: volatile liquids in air.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 858,
Issue. ,
p.
881.
Bhat, Maanasa
and
Sivakumar, D.
2019.
Post-spreading behavior of impacting fuel drops on stainless steel surface.
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science,
Vol. 102,
Issue. ,
p.
74.
Sadafi, Hosein
Dehaeck, Sam
Rednikov, Alexey
and
Colinet, Pierre
2019.
Vapor-Mediated versus Substrate-Mediated Interactions between Volatile Droplets.
Langmuir,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 21,
p.
7060.
Wolf, Christian
and
Gambaryan-Roisman, Tatiana
2020.
Wetting and Evaporation of Solvents on Thin Soluble Substrates.
Colloids and Interfaces,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 4,
p.
48.
Rednikov, A. Ye.
and
Colinet, P.
2020.
Contact angles for perfectly wetting pure liquids evaporating into air: Between de Gennes-type and other classical models.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 11,
Jeong, Chan Ho
Lee, Hyung Ju
Kim, Dae Yun
Ahangar, Shahab Bayani
Choi, Chang Kyoung
and
Lee, Seong Hyuk
2021.
Quantitative analysis of contact line behaviors of evaporating binary mixture droplets using surface plasmon resonance imaging.
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Vol. 165,
Issue. ,
p.
120690.
Shiri, Samira
Sinha, Shayandev
Baumgartner, Dieter A.
and
Cira, Nate J.
2021.
Thermal Marangoni Flow Impacts the Shape of Single Component Volatile Droplets on Thin, Completely Wetting Substrates.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 127,
Issue. 2,
Pahlavan, Amir A.
Yang, Lisong
Bain, Colin D.
and
Stone, Howard A.
2021.
Evaporation of Binary-Mixture Liquid Droplets: The Formation of Picoliter Pancakelike Shapes.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 127,
Issue. 2,
Schulz, Florian
Duill, Finn Felix
Hajhariri, Aliasghar
and
Beyrau, Frank
2021.
The Behavior of Fuel Droplets on a Heated Substrate.
Vol. 1,
Issue. ,
Wu, Mengmeng
Doi, Masao
and
Man, Xingkun
2021.
The contact angle of an evaporating droplet of a binary solution on a super wetting surface.
Soft Matter,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 34,
p.
7932.
Mitchell, Jimmie
and
Weimer, Jeffrey J.
2021.
Controlled Spreading Rates to Distribute Nanoparticles as Uniform Langmuir Films.
Langmuir,
Vol. 37,
Issue. 17,
p.
5139.
Kumar, Satish
and
Charitatos, Vasileios
2022.
Influence of Surface Roughness on Droplet Evaporation and Absorption: Insights into Experiments from Lubrication-Theory-Based Models.
Langmuir,
Vol. 38,
Issue. 51,
p.
15889.
Yang, Xiuyuan
Wu, MengMeng
Doi, Masao
and
Man, Xingkun
2022.
Evaporation Dynamics of Sessile Droplets: The Intricate Coupling of Capillary, Evaporation, and Marangoni Flow.
Langmuir,
Vol. 38,
Issue. 16,
p.
4887.
Saiseau, Raphael
Pedersen, Christian
Benjana, Anwar
Carlson, Andreas
Delabre, Ulysse
Salez, Thomas
and
Delville, Jean-Pierre
2022.
Near-critical spreading of droplets.
Nature Communications,
Vol. 13,
Issue. 1,
Kap, Özlem
Hartmann, Simon
Hoek, Harmen
de Beer, Sissi
Siretanu, Igor
Thiele, Uwe
and
Mugele, Frieder
2023.
Nonequilibrium configurations of swelling polymer brush layers induced by spreading drops of weakly volatile oil.
The Journal of Chemical Physics,
Vol. 158,
Issue. 17,
Moore, Madeleine R.
and
Wray, Alexander W.
2023.
Gravitational effects on coffee-ring formation during the evaporation of sessile droplets.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 967,
Issue. ,
Larsson, Christopher
and
Kumar, Satish
2023.
Comparison of one-sided and diffusion-limited evaporation models for thin liquid droplets.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 976,
Issue. ,
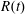 $R(t)$ of completely wetting alkane drops of different volatility on glass. Initially the drop spreads (
$R(t)$ of completely wetting alkane drops of different volatility on glass. Initially the drop spreads (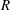 $R$ increases), then owing to evaporation reverses direction and recedes with an almost constant non-zero contact angle
$R$ increases), then owing to evaporation reverses direction and recedes with an almost constant non-zero contact angle 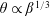 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}\propto \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}^{1/3}$, where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}\propto \unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}^{1/3}$, where 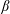 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$ measures the rate of evaporation; eventually the drop vanishes at a finite-time singularity. Our theory, based on a first-principles hydrodynamic description, well reproduces the dynamics of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$ measures the rate of evaporation; eventually the drop vanishes at a finite-time singularity. Our theory, based on a first-principles hydrodynamic description, well reproduces the dynamics of 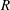 $R$ and the value of
$R$ and the value of 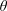 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$ during retraction.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$ during retraction.

