1. Introduction
Drop-on-demand inkjet printing is known for its capability of highly controlled, non-contact deposition of picolitres of liquid material (Basaran Reference Basaran2002; Derby Reference Derby2010; Wijshoff Reference Wijshoff2010; Hoath Reference Hoath2016; Lohse Reference Lohse2022). Recent advances have enabled and enhanced our ability to deposit liquids over a wide range of surface tensions and viscosities (Castrejón-Pita et al. Reference Castrejón-Pita, Baxter, Morgan, Temple, Martin and Hutchings2013). The high degree of reproducibility has led to inkjet printing being employed in a diverse array of applications, including text or graphical printing on paper, fabrication of displays in electronics (Shimoda et al. Reference Shimoda, Morii, Seki and Kiguchi2003), electronics printing (Majee et al. Reference Majee, Song, Zhang and Zhang2016, Reference Majee, Liu, Wu, Zhang and Zhang2017) with applications also in the life sciences (Villar, Graham & Bayley Reference Villar, Graham and Bayley2013; Daly et al. Reference Daly, Harrington, Martin and Hutchings2015; Simaite et al. Reference Simaite, Mesnilgrente, Tondu, Souères and Bergaud2016).
A typical inkjet printhead primarily consists of an ink reservoir, a piezo-acoustic transducer and a dispensing nozzle (Wijshoff Reference Wijshoff2010), while the most simple driving waveform is a monopolar trapezoidal pulse (Castrejón-Pita et al. Reference Castrejón-Pita, Martin, Hoath and Hutchings2008), with a pulse width equal to half the period corresponding to the resonance frequency. Inkjet printheads are usually operated in the ‘pull–push’ mode, where the liquid is first pulled into the nozzle during the rise time of the trapezoidal pulse and then pushed out during the fall time of the pulse (Fraters et al. Reference Fraters, Jeurissen, van der Berg, Reinten, Wijshoff, Lohse, Versluis and Segers2020). This results in the creation of a slender liquid jet of finite length and after pinch-off from the nozzle, a finite liquid ligament with a relatively large head droplet and a long tail. As the ligament is travelling towards the substrate, the tail retracts into the head droplet due to surface tension. However, during such motion, the tail may also break up due to the Rayleigh–Plateau instability (Fraters et al. Reference Fraters, Jeurissen, van der Berg, Reinten, Wijshoff, Lohse, Versluis and Segers2020). This breakup leads to the formation of satellite droplets, which travel at a velocity lower than that of the head droplet. Thus the head droplet and the satellite droplet(s) reach the substrate at different times, potentially resulting in misalignment and substantially reduced print quality (Derby Reference Derby2010; Wijshoff Reference Wijshoff2010), and contamination within the print device.
The detrimental effect of the formation of satellite droplets has resulted in an increased focus on the development of techniques to suppress such satellites. These techniques are either based on changing the driving waveform (Dong, Carr & Morris Reference Dong, Carr and Morris2006; Fraters et al. Reference Fraters, Jeurissen, van der Berg, Reinten, Wijshoff, Lohse, Versluis and Segers2020) or modifying the properties of the ink. For the latter, since the satellite droplets primarily result from a Rayleigh–Plateau instability of the retracting tail, an obvious choice is to increase the viscosity of the ink in order to stabilize the tail filament (Notz & Basaran Reference Notz and Basaran2004; Castrejón-Pita, Castrejón-Pita & Hutchings Reference Castrejón-Pita, Castrejón-Pita and Hutchings2012; Driessen et al. Reference Driessen, Jeurissen, Wijshoff, Toschi and Lohse2013; Anthony et al. Reference Anthony, Kamat, Harris and Basaran2019; Planchette et al. Reference Planchette, Marangon, Hsiao and Brenn2019; Wang et al. Reference Wang, Contò, Naz, Castrejón-Pita, Castrejón-Pita, Bailey, Wang, Feng and Sui2019).
Another strategy (Christanti & Walker Reference Christanti and Walker2002) for the suppression of satellite droplet formation is to include polymer additives, which impart viscoelasticity, in the liquid being jetted. Early work has shown that viscoelasticity can stabilize a capillary jet against breakup (Goldin et al. Reference Goldin, Yerushalmi, Pfeffer and Shinnar1969), and can also suppress satellite droplets when the liquid is jetted by a forced disturbance (such as in inkjet printing) (Christanti & Walker Reference Christanti and Walker2002). Shore & Harrison (Reference Shore and Harrison2005) experimentally demonstrated that the addition of polymers to water-based inks suppresses satellite droplet formation in an inkjet printing configuration, while the same observation was also reported in the numerical investigation by Morrison & Harlen (Reference Morrison and Harlen2010). Yan, Carr & Dong (Reference Yan, Carr and Dong2011) studied the effect of adding polymers, specifically polyethylene oxide (PEO), to water-based inks in inkjet printing, and concluded that the addition of low molecular weight polymers has no significant effect on the overall dynamics of the jetting behaviour. Hoath, Harlen & Hutchings (Reference Hoath, Harlen and Hutchings2012) identified experimentally scaling laws relating the maximum jettable concentration to the molecular weight of the polymer additive for polystyrene in diethyl phthalate solutions. For these polymer solutions, it was also reported (Hoath et al. Reference Hoath, Vadillo, Harlen, McIlroy, Morrison, Hsiao, Tuladhar, Jung, Martin and Hutchings2014) that there is a delay in the pinch-off of the liquid filament from the nozzle, as compared with a purely Newtonian ink.
Despite the recent surge in the investigations of inkjet printing with polymer solutions, and the extensive literature (Bazilevskii, Entov & Rozhkov Reference Bazilevskii, Entov and Rozhkov1990; Amarouchene et al. Reference Amarouchene, Bonn, Meunier and Kellay2001; Anna & McKinley Reference Anna and McKinley2001; Clasen et al. Reference Clasen, Eggers, Fontelos, Li and McKinley2006a; Zhou & Doi Reference Zhou and Doi2018, Reference Zhou and Doi2020; Eggers, Herrada & Snoeijer Reference Eggers, Herrada and Snoeijer2020) on the thinning and breakup of polymeric jets and pendant drops, there seems to be a dearth in the quantitative understanding of the fundamental physical mechanisms responsible for the suppression of satellite droplets in such conditions. Here, we quantitatively study the breakup (or retraction) of the long ligaments produced during (polymeric) ink jetting and the subsequent satellite droplet formation (or suppression). In particular, we identify the operating range where no satellite droplets are observed. In this range, the temporal retraction behaviour of the jetted ligament length is characterized, and explained by a simple theoretical model. The model also quantifies the forces responsible for the suppression of satellite droplets, and demonstrates reasonable agreement with the experimental observations.
The paper is organized as follows: § 2 describes the experimental procedure. In § 3 the experimental results for different values of the control parameters are shown, culminating in the phase diagram (figure 4). In § 4 we present detailed and quantitative experimental measurements of the filament retraction, which are theoretically explained in § 5. The paper ends with conclusions and an outlook in § 6.
2. Experimental procedure
Along the lines of previous work (Christanti & Walker Reference Christanti and Walker2002; Shore & Harrison Reference Shore and Harrison2005; Yan et al. Reference Yan, Carr and Dong2011), PEO (average molecular weight ![]() ${\simeq }10^{6}$ a.u., Sigma-Aldrich, henceforth referred to as PEO1M) was chosen to be the polymer additive in this work. Aqueous solutions of PEO1M, of concentration (
${\simeq }10^{6}$ a.u., Sigma-Aldrich, henceforth referred to as PEO1M) was chosen to be the polymer additive in this work. Aqueous solutions of PEO1M, of concentration (![]() $c$, by mass) ranging from 0.001 % to 0.009 %, were prepared by adding the required amount of polymer powder to purified water (Milli-Q). For each polymer concentration, a 100 ml solution is made at first and all experiments were carried out using the same solution. The required polymer powder amount was measured using a precision laboratory balance (Secura 224-1S, Sartorius) with an accuracy of 0.1 mg, and then added to purified water (Milli-Q). Each solution was stirred with a magnetic stirrer for 24 h prior to use in order to ensure homogeneity of concentration. This results in a high degree of repeatability of the experiments (as evident later from the small error bars in figure 5a). In the present experiments, we wanted to have polymer solutions that can act as Boger fluids (James Reference James2009), i.e. solutions whose shear viscosities are independent of the shear rate. This allows for the development of the simplified model, shown in § 5, where the shear rate dependence on viscosity is not taken into account. Dilute aqueous solutions of PEO1M act as Boger fluids (Cooper-White et al. Reference Cooper-White, Fagan, Tirtaatmadja, Lester and Boger2002). Thus PEO1M was chosen as the polymer to be tested. This was also verified independently in the present work. The rheological characterization of the test liquids was performed on a rotational rheometer (MCR 502, Anton-Paar) with a cone-and-plate configuration (1
$c$, by mass) ranging from 0.001 % to 0.009 %, were prepared by adding the required amount of polymer powder to purified water (Milli-Q). For each polymer concentration, a 100 ml solution is made at first and all experiments were carried out using the same solution. The required polymer powder amount was measured using a precision laboratory balance (Secura 224-1S, Sartorius) with an accuracy of 0.1 mg, and then added to purified water (Milli-Q). Each solution was stirred with a magnetic stirrer for 24 h prior to use in order to ensure homogeneity of concentration. This results in a high degree of repeatability of the experiments (as evident later from the small error bars in figure 5a). In the present experiments, we wanted to have polymer solutions that can act as Boger fluids (James Reference James2009), i.e. solutions whose shear viscosities are independent of the shear rate. This allows for the development of the simplified model, shown in § 5, where the shear rate dependence on viscosity is not taken into account. Dilute aqueous solutions of PEO1M act as Boger fluids (Cooper-White et al. Reference Cooper-White, Fagan, Tirtaatmadja, Lester and Boger2002). Thus PEO1M was chosen as the polymer to be tested. This was also verified independently in the present work. The rheological characterization of the test liquids was performed on a rotational rheometer (MCR 502, Anton-Paar) with a cone-and-plate configuration (1![]() $^{\circ }$ angle, 50 mm diameter and mean gap of 0.1 mm). The measured viscosities are mentioned in table 1, where
$^{\circ }$ angle, 50 mm diameter and mean gap of 0.1 mm). The measured viscosities are mentioned in table 1, where ![]() $c^{\ast }$ is the critical overlap concentration (Clasen et al. Reference Clasen, Plog, Kulicke, Owens, Macosko, Scriven, Verani and McKinley2006b). That being said, the results of the present work, in particular the simplified theoretical model (§ 5), can be extended to any Boger fluid composed of a different polymer. This can be easily facilitated by characterizing the rheological properties of the test fluid such as relaxation time (
$c^{\ast }$ is the critical overlap concentration (Clasen et al. Reference Clasen, Plog, Kulicke, Owens, Macosko, Scriven, Verani and McKinley2006b). That being said, the results of the present work, in particular the simplified theoretical model (§ 5), can be extended to any Boger fluid composed of a different polymer. This can be easily facilitated by characterizing the rheological properties of the test fluid such as relaxation time (![]() $\lambda$), solvent (
$\lambda$), solvent (![]() $\eta _{s}$) and polymer (
$\eta _{s}$) and polymer (![]() $\eta _{p}$) viscosities, along with knowing the density (
$\eta _{p}$) viscosities, along with knowing the density (![]() $\rho$) and surface tension (
$\rho$) and surface tension (![]() $\gamma$). These material properties can then be incorporated into the theoretical approach (§ 5). The relaxation times were measured from the extensional thinning of the liquid filaments in a pendant droplet configuration (Deblais, Velikov & Bonn Reference Deblais, Velikov and Bonn2018; Deblais et al. Reference Deblais, Herrada, Eggers and Bonn2020) (see also relaxation time measurement in a capillary breakup extension rheometer (CaBER) device: Bazilevskii et al. Reference Bazilevskii, Entov and Rozhkov1990; Amarouchene et al. Reference Amarouchene, Bonn, Meunier and Kellay2001; Anna & McKinley Reference Anna and McKinley2001; Clasen et al. Reference Clasen, Eggers, Fontelos, Li and McKinley2006a). The surface tension was measured by the pendant droplet method in an optical contact angle measurement and contour analysis instrument (OCA15, Dataphysics). It was noted that the surface tensions and the viscosities for the solutions of different polymer concentrations remained practically unchanged, while an appreciable change was observed in the relaxation time measurements (also observed by Yan et al. Reference Yan, Carr and Dong2011). Furthermore, it is known from the literature (Noskov et al. Reference Noskov, Akentiev, Loglio and Miller2000) that changing the PEO concentration can change the surface properties of the solutions. However, in the very narrow concentration range (0.001 %–0.009 % by wt.) used in the present work, the surface properties are practically independent of the polymer concentration (Noskov et al. Reference Noskov, Akentiev, Loglio and Miller2000). Hence the surface properties of the solution were not taken into account. Nonetheless, it would be an interesting study to see how the surface properties of the solution affect the filament stability, and some recent numerical studies (Kamat et al. Reference Kamat, Wagoner, Castrejón-Pita, Castrejón-Pita, Anthony and Basaran2020; Wee et al. Reference Wee, Wagoner, Kamat and Basaran2020, Reference Wee, Wagoner, Garg, Kamat and Basaran2021) have already provided an indication of significant effects of surface properties. However, a detailed experimental study investigating the effects of the surface properties is beyond the scope of the present work. A recent study (Walls, Henaux & Bird Reference Walls, Henaux and Bird2015) also suggests that the viscosity of the outer gas can play a role in the breakup of a liquid filament. However, the focus of the present work is to study the effect of viscoelasticity on the retraction of a liquid filament. In that context, the effect of the outer gas viscosity is also not within the scope of the current study. Therefore, experiments with different surrounding gases were not performed.
$\gamma$). These material properties can then be incorporated into the theoretical approach (§ 5). The relaxation times were measured from the extensional thinning of the liquid filaments in a pendant droplet configuration (Deblais, Velikov & Bonn Reference Deblais, Velikov and Bonn2018; Deblais et al. Reference Deblais, Herrada, Eggers and Bonn2020) (see also relaxation time measurement in a capillary breakup extension rheometer (CaBER) device: Bazilevskii et al. Reference Bazilevskii, Entov and Rozhkov1990; Amarouchene et al. Reference Amarouchene, Bonn, Meunier and Kellay2001; Anna & McKinley Reference Anna and McKinley2001; Clasen et al. Reference Clasen, Eggers, Fontelos, Li and McKinley2006a). The surface tension was measured by the pendant droplet method in an optical contact angle measurement and contour analysis instrument (OCA15, Dataphysics). It was noted that the surface tensions and the viscosities for the solutions of different polymer concentrations remained practically unchanged, while an appreciable change was observed in the relaxation time measurements (also observed by Yan et al. Reference Yan, Carr and Dong2011). Furthermore, it is known from the literature (Noskov et al. Reference Noskov, Akentiev, Loglio and Miller2000) that changing the PEO concentration can change the surface properties of the solutions. However, in the very narrow concentration range (0.001 %–0.009 % by wt.) used in the present work, the surface properties are practically independent of the polymer concentration (Noskov et al. Reference Noskov, Akentiev, Loglio and Miller2000). Hence the surface properties of the solution were not taken into account. Nonetheless, it would be an interesting study to see how the surface properties of the solution affect the filament stability, and some recent numerical studies (Kamat et al. Reference Kamat, Wagoner, Castrejón-Pita, Castrejón-Pita, Anthony and Basaran2020; Wee et al. Reference Wee, Wagoner, Kamat and Basaran2020, Reference Wee, Wagoner, Garg, Kamat and Basaran2021) have already provided an indication of significant effects of surface properties. However, a detailed experimental study investigating the effects of the surface properties is beyond the scope of the present work. A recent study (Walls, Henaux & Bird Reference Walls, Henaux and Bird2015) also suggests that the viscosity of the outer gas can play a role in the breakup of a liquid filament. However, the focus of the present work is to study the effect of viscoelasticity on the retraction of a liquid filament. In that context, the effect of the outer gas viscosity is also not within the scope of the current study. Therefore, experiments with different surrounding gases were not performed.
Table 1. Salient properties of the PEO1M solutions used in the present work.

The schematic of the experimental set-up is shown in figure 1(a) (a photograph of the set-up has been provided as part of the supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2021.855). A microdrop dispenser (AD-K-501, Microdrop Technologies GmbH), with a nozzle inner diameter of 50 ![]() $\mathrm {\mu }$m was used to generate the liquid ligaments. The dispenser consists of a cylindrical piezoacoustic transducer glued around a glass capillary connected to a fluid reservoir. A detailed description of such a dispenser can be found in Dijksman (Reference Dijksman1984) and Fraters et al. (Reference Fraters2021). The piezoacoustic element is driven by an electrical pulse supplied from an arbitrary waveform generator (WW1072, Tabor Electronics) and amplified (50
$\mathrm {\mu }$m was used to generate the liquid ligaments. The dispenser consists of a cylindrical piezoacoustic transducer glued around a glass capillary connected to a fluid reservoir. A detailed description of such a dispenser can be found in Dijksman (Reference Dijksman1984) and Fraters et al. (Reference Fraters2021). The piezoacoustic element is driven by an electrical pulse supplied from an arbitrary waveform generator (WW1072, Tabor Electronics) and amplified (50![]() $\times$) by a high-voltage amplifier (WMA-300, Falco Systems). A typical driving electrical pulse is trapezoidal in shape (Wijshoff Reference Wijshoff2010), as shown in figure 1(b), where
$\times$) by a high-voltage amplifier (WMA-300, Falco Systems). A typical driving electrical pulse is trapezoidal in shape (Wijshoff Reference Wijshoff2010), as shown in figure 1(b), where ![]() $V_{A}$ denotes voltage and
$V_{A}$ denotes voltage and ![]() $t$ denotes time. The rise and fall times of the pulse are kept constant in the present experiments at 1
$t$ denotes time. The rise and fall times of the pulse are kept constant in the present experiments at 1 ![]() $\mathrm {\mu }$s, while the amplitude (
$\mathrm {\mu }$s, while the amplitude (![]() $V_{A,max}$) and the pulse width (
$V_{A,max}$) and the pulse width (![]() $t_{w}$) were varied in the ranges 50–75 V and 30–50
$t_{w}$) were varied in the ranges 50–75 V and 30–50 ![]() $\mathrm {\mu }$s, respectively. The lower limits of these ranges are set by the minimum driving required for jetting, while the upper limits are dictated by a bubble entrainment phenomenon associated with meniscus destabilization at strong driving conditions (Fraters et al. Reference Fraters, van der Berg, de Loore, Reinten, Wijshoff, Lohse, Versluis and Segers2019, Reference Fraters2021). The shape of the supply waveform was verified by an oscilloscope (DPO 4034B, Tektronix). The liquid in the dispenser was supplied from a transparent plastic syringe (5 ml, Becton-Dickinson) connected via a flexible plastic PEEK tubing (Upchurch Scientific). The microdrop dispenser was driven continuously at a drop-on-demand frequency of 100 Hz to minimize selective evaporation from the nozzle, thereby ensuring a constant liquid composition. High-speed imaging of the jetting behaviour was performed at 10
$\mathrm {\mu }$s, respectively. The lower limits of these ranges are set by the minimum driving required for jetting, while the upper limits are dictated by a bubble entrainment phenomenon associated with meniscus destabilization at strong driving conditions (Fraters et al. Reference Fraters, van der Berg, de Loore, Reinten, Wijshoff, Lohse, Versluis and Segers2019, Reference Fraters2021). The shape of the supply waveform was verified by an oscilloscope (DPO 4034B, Tektronix). The liquid in the dispenser was supplied from a transparent plastic syringe (5 ml, Becton-Dickinson) connected via a flexible plastic PEEK tubing (Upchurch Scientific). The microdrop dispenser was driven continuously at a drop-on-demand frequency of 100 Hz to minimize selective evaporation from the nozzle, thereby ensuring a constant liquid composition. High-speed imaging of the jetting behaviour was performed at 10![]() $^{5}$ frames per second, with a 600 ns exposure time, by a high-speed camera (Fastcam SA-Z, Photron) connected to a modular microscope (U-ECA and BXFM-F, Olympus) with multiple objectives (
$^{5}$ frames per second, with a 600 ns exposure time, by a high-speed camera (Fastcam SA-Z, Photron) connected to a modular microscope (U-ECA and BXFM-F, Olympus) with multiple objectives (![]() ${\times}$ 5,
${\times}$ 5, ![]() ${\times}$ 10 and
${\times}$ 10 and ![]() ${\times}$ 20, MPlanFL N, Olympus). This allowed for a spatial resolution of as low as 1
${\times}$ 20, MPlanFL N, Olympus). This allowed for a spatial resolution of as low as 1 ![]() $\mathrm {\mu }$m per pixel. The experiments were illuminated by a LED light source (70 % intensity, KL 2500 LED, Schott), with the light beam being collimated onto the imaging plane by a collimation lens (Thorlabs). The light source used in the present work is a cold light source, and was only used at 70 % of its maximum intensity. Furthermore, the light source would only be switched on during image capturing, and remained switched off when the camera was not capturing any frames (such as during changing or refilling the liquid, and saving the captured frames on the computer hard drive). Thus it is expected that the temperature of the liquid in the device does not change appreciably due to the presence of the light source. The dispenser and the camera were triggered simultaneously (with nanosecond precision) by a programmable pulse-delay generator (BNC 575, Berkley Nucleonics Corp.). The captured images were further analysed using an OpenCV-based Python script developed in house. The script utilized a Canny edge detection method to find the edges of the jetted ligament outside the nozzle and that of the retracting meniscus within the nozzle. Knowing the pixel location of the edges, one can find the top-most and bottom-most points of the jetted ligament, and thus its length (defined as
$\mathrm {\mu }$m per pixel. The experiments were illuminated by a LED light source (70 % intensity, KL 2500 LED, Schott), with the light beam being collimated onto the imaging plane by a collimation lens (Thorlabs). The light source used in the present work is a cold light source, and was only used at 70 % of its maximum intensity. Furthermore, the light source would only be switched on during image capturing, and remained switched off when the camera was not capturing any frames (such as during changing or refilling the liquid, and saving the captured frames on the computer hard drive). Thus it is expected that the temperature of the liquid in the device does not change appreciably due to the presence of the light source. The dispenser and the camera were triggered simultaneously (with nanosecond precision) by a programmable pulse-delay generator (BNC 575, Berkley Nucleonics Corp.). The captured images were further analysed using an OpenCV-based Python script developed in house. The script utilized a Canny edge detection method to find the edges of the jetted ligament outside the nozzle and that of the retracting meniscus within the nozzle. Knowing the pixel location of the edges, one can find the top-most and bottom-most points of the jetted ligament, and thus its length (defined as ![]() $L(t)$ in figure 5a). Similarly, knowing the top-most point of the retracting meniscus within the nozzle,
$L(t)$ in figure 5a). Similarly, knowing the top-most point of the retracting meniscus within the nozzle, ![]() $z_{m}$ (figure 3d), is tracked.
$z_{m}$ (figure 3d), is tracked.

Figure 1. (a) Schematic of the experimental set-up. (b) Typical trapezoidal pulse used for actuation. (c) Jetting with water at ![]() $V_{A, max} = 50$ V,
$V_{A, max} = 50$ V, ![]() $t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s results in a single droplet. (d) Jetting with water at
$t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s results in a single droplet. (d) Jetting with water at ![]() $V_{A, max}= 60$ V,
$V_{A, max}= 60$ V, ![]() $t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s results in the formation of a primary droplet and a satellite droplet.
$t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s results in the formation of a primary droplet and a satellite droplet.
3. Jetting liquids with polymer additives
The jetting behaviour with water at ![]() $V_{A, max}= 50$ V,
$V_{A, max}= 50$ V, ![]() $t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s is shown in figure 1(c) (and supplementary movie 1 available at https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2021.855). Here, and in all subsequent figures, the time
$t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s is shown in figure 1(c) (and supplementary movie 1 available at https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2021.855). Here, and in all subsequent figures, the time ![]() $t = 0$ is defined as the moment when the dispenser is triggered. At that moment, the recording with the camera is also started. A detailed description of the inkjet droplet formation can be found in Hoath (Reference Hoath2016) and Wijshoff (Reference Wijshoff2010). Briefly, a liquid ligament is formed following pinch-off from the nozzle. As the ligament propagates, the tail retracts due to capillarity, and merges with the head droplet to form a single droplet. When the pulse amplitude (
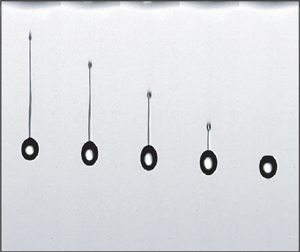
$t = 0$ is defined as the moment when the dispenser is triggered. At that moment, the recording with the camera is also started. A detailed description of the inkjet droplet formation can be found in Hoath (Reference Hoath2016) and Wijshoff (Reference Wijshoff2010). Briefly, a liquid ligament is formed following pinch-off from the nozzle. As the ligament propagates, the tail retracts due to capillarity, and merges with the head droplet to form a single droplet. When the pulse amplitude (![]() $V_{A, max}$) is further increased to 60 V, a longer ligament is initially produced (as seen in figure 1(d) and supplementary movie 1); however, in this case, the tail does not retract into the head droplet. Instead, the ligament breaks up into multiple smaller droplets through the Rayleigh–Plateau instability. These smaller droplets in figure 1(d) then merge to form a larger satellite droplet, which never coalesces with the primary droplet owing to the satellite's lower speed.
$V_{A, max}$) is further increased to 60 V, a longer ligament is initially produced (as seen in figure 1(d) and supplementary movie 1); however, in this case, the tail does not retract into the head droplet. Instead, the ligament breaks up into multiple smaller droplets through the Rayleigh–Plateau instability. These smaller droplets in figure 1(d) then merge to form a larger satellite droplet, which never coalesces with the primary droplet owing to the satellite's lower speed.
Next, we add the polymer (PEO1M) to the fluid being jetted. The typical jetting behaviour for three different concentrations is shown in figure 2. In all the three cases shown in the figure, the driving conditions are kept constant at ![]() $V_{A, max} = 60$ V,
$V_{A, max} = 60$ V, ![]() $t_{w}=40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s; only the concentration of PEO1M is varied. The jetting behaviour with water at this condition is shown in figure 2(a), reproduced from figure 1(d). For the 0.003 % PEO1M solution (figure 2(b) and supplementary movie 2), the jetting behaviour shows a stark difference as compared with that of water. Now the jetted ligament consists again of a spherical head droplet and a long slender tail, similar to the pure water case. Note that the tail here is significantly thinner than the one for the weaker driving case with water (figure 1c). A small spherical tail droplet is also observed in this case, which grows in size as the tail retracts towards the head droplet. When the head and the tail droplet are sufficiently close, they merge to form a single droplet, without any satellite droplets being formed. Thus, the addition of a very small quantity of PEO1M (0.003 % by mass) is sufficient to suppress the formation of satellite droplets. Addition of the long chain polymer imparts viscoelasticity to the aqueous solution. The slender tail acts like a stretched filament, being forced by elasticity (and capillarity) to retract its length. This results in the retraction of the whole liquid filament without any intermediate break up. By observing the time stamps, it can also be identified that the pinch-off from the nozzle happens at a later time for the 0.003 % PEO1M solution (0.22 ms) as compared with that for water (0.15 ms). This has been reported in Hoath et al. (Reference Hoath, Vadillo, Harlen, McIlroy, Morrison, Hsiao, Tuladhar, Jung, Martin and Hutchings2014) also, albeit for a different polymer–solvent combination. We note that the suppression of satellite droplet formation by the addition of viscoelasticity comes at the cost of some jetting velocity. For example, the velocity of the jetted 0.003 % PEO1M droplet (figure 2b) was measured to be 3.11 m s
$t_{w}=40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s; only the concentration of PEO1M is varied. The jetting behaviour with water at this condition is shown in figure 2(a), reproduced from figure 1(d). For the 0.003 % PEO1M solution (figure 2(b) and supplementary movie 2), the jetting behaviour shows a stark difference as compared with that of water. Now the jetted ligament consists again of a spherical head droplet and a long slender tail, similar to the pure water case. Note that the tail here is significantly thinner than the one for the weaker driving case with water (figure 1c). A small spherical tail droplet is also observed in this case, which grows in size as the tail retracts towards the head droplet. When the head and the tail droplet are sufficiently close, they merge to form a single droplet, without any satellite droplets being formed. Thus, the addition of a very small quantity of PEO1M (0.003 % by mass) is sufficient to suppress the formation of satellite droplets. Addition of the long chain polymer imparts viscoelasticity to the aqueous solution. The slender tail acts like a stretched filament, being forced by elasticity (and capillarity) to retract its length. This results in the retraction of the whole liquid filament without any intermediate break up. By observing the time stamps, it can also be identified that the pinch-off from the nozzle happens at a later time for the 0.003 % PEO1M solution (0.22 ms) as compared with that for water (0.15 ms). This has been reported in Hoath et al. (Reference Hoath, Vadillo, Harlen, McIlroy, Morrison, Hsiao, Tuladhar, Jung, Martin and Hutchings2014) also, albeit for a different polymer–solvent combination. We note that the suppression of satellite droplet formation by the addition of viscoelasticity comes at the cost of some jetting velocity. For example, the velocity of the jetted 0.003 % PEO1M droplet (figure 2b) was measured to be 3.11 m s![]() $^{-1}$, as compared with the 3.33 m s
$^{-1}$, as compared with the 3.33 m s![]() $^{-1}$ measured for the primary droplet in the pure water case (figure 2a). A hypothesis for this decrease in velocity is as follows: in a piezo-acoustic fluid dispenser such as the one used in the present work, the electrical pulse input to the transducer induces a mechanical deformation of the piezo-actuator, resulting in a pressure pulse in the liquid within the dispenser. A detailed description of the associated mechanisms can be found in Dijksman (Reference Dijksman1984) and Wijshoff (Reference Wijshoff2010). From an energetics point of view, the pressure pulse imparts an additional energy in the fluid volume. For a Newtonian liquid, this energy is converted into the surface energy of the jetted droplet and its kinetic energy. However, for a viscoelastic liquid, there is an additional elastic energy associated with stretching the liquid ligament. Since the droplet sizes for the Newtonian and the viscoelastic cases are almost the same, resulting in similar surface energies (as surface tension remains unchanged at such low polymer concentration, as seen in table 1), the resulting kinetic energy for the viscoelastic droplet is lower. This results in a lower jetting velocity. However, this is only a qualitative understanding of the physical phenomenon, and a detailed quantitative understanding is beyond the scope of the present work.
$^{-1}$ measured for the primary droplet in the pure water case (figure 2a). A hypothesis for this decrease in velocity is as follows: in a piezo-acoustic fluid dispenser such as the one used in the present work, the electrical pulse input to the transducer induces a mechanical deformation of the piezo-actuator, resulting in a pressure pulse in the liquid within the dispenser. A detailed description of the associated mechanisms can be found in Dijksman (Reference Dijksman1984) and Wijshoff (Reference Wijshoff2010). From an energetics point of view, the pressure pulse imparts an additional energy in the fluid volume. For a Newtonian liquid, this energy is converted into the surface energy of the jetted droplet and its kinetic energy. However, for a viscoelastic liquid, there is an additional elastic energy associated with stretching the liquid ligament. Since the droplet sizes for the Newtonian and the viscoelastic cases are almost the same, resulting in similar surface energies (as surface tension remains unchanged at such low polymer concentration, as seen in table 1), the resulting kinetic energy for the viscoelastic droplet is lower. This results in a lower jetting velocity. However, this is only a qualitative understanding of the physical phenomenon, and a detailed quantitative understanding is beyond the scope of the present work.

Figure 2. (a) Jetting with water at ![]() $V_{A, max} = 60$ V,
$V_{A, max} = 60$ V, ![]() $t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s results in the formation of a satellite droplet (‘satellite’ regime). (b) Jetting with 0.003 % PEO1M solution (
$t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s results in the formation of a satellite droplet (‘satellite’ regime). (b) Jetting with 0.003 % PEO1M solution (![]() $\lambda =28.2$ ms,
$\lambda =28.2$ ms, ![]() $c/c^{\ast }=0.022$, nozzle Deborah number
$c/c^{\ast }=0.022$, nozzle Deborah number ![]() $(De_{n})=1.91$) at
$(De_{n})=1.91$) at ![]() $V_{A, max} = 60$ V,
$V_{A, max} = 60$ V, ![]() $t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s results in the suppression of satellite droplet formation (‘no satellite’ regime). (c) A 0.009 % PEO1M solution (
$t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s results in the suppression of satellite droplet formation (‘no satellite’ regime). (c) A 0.009 % PEO1M solution (![]() $\lambda =99.38$ ms,
$\lambda =99.38$ ms, ![]() $c/c^{\ast }=0.067$,
$c/c^{\ast }=0.067$, ![]() $De_{n}=6.75$) at
$De_{n}=6.75$) at ![]() $V_{A, max} = 60$ V,
$V_{A, max} = 60$ V, ![]() $t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s results in no detachment of droplets from the nozzle (‘no jetting’ regime).
$t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s results in no detachment of droplets from the nozzle (‘no jetting’ regime).
If the polymer concentration is further increased to 0.009 % by mass (still with the same driving), the jetting behaviour again changes dramatically, as seen in figure 2(c) (and supplementary movie 2). In this case, a filament of the liquid, while still connected to the liquid inside the nozzle, appears downstream of the nozzle exit. However, now the additional polymer content has increased the elasticity to such an extent that the filament does not pinch-off from the nozzle. Instead, it retracts back into the nozzle, thus suppressing jetting altogether. Morrison & Harlen (Reference Morrison and Harlen2010) refer to such observations as the ‘bungee jumper’ in their numerical study. Obviously, for inkjet printing or similar droplet deposition applications, this phenomenon is undesirable, as no droplet is being produced.
The vastly different jetting behaviours observed in figure 2 suggest that, for a given driving condition, there exists a concentration range where jetting without the formation of satellites is observed, and on either side of that range the jetting deteriorates, namely by the occurrence of satellites for lower concentrations, or by suppressing the jetting altogether at high concentrations. Hence it is imperative to delineate these three regimes in an appropriate two-dimensional parameter space, with suitable variables representing the solution concentrations and the driving conditions.
The choice of the control parameter to represent the driving condition is not straightforward, as both pulse amplitude (![]() $V_{A, max}$) and pulse width (
$V_{A, max}$) and pulse width (![]() $t_{w}$) are varied in the present experiments. Since the optically transparent microdrop dispenser is operated in the ‘pull–push’ mode, the motion of the liquid meniscus inside the nozzle, just prior to filament pinch-off, can be observed in order to gauge the effect of the driving condition. The meniscus motion for three different solution concentrations, at the same driving condition, are shown in figure 3 (and supplementary movie 3). A detailed description of such motion, and how it is affected by changing the driving conditions, can be found in Fraters et al. (Reference Fraters2021). The position of the meniscus,
$t_{w}$) are varied in the present experiments. Since the optically transparent microdrop dispenser is operated in the ‘pull–push’ mode, the motion of the liquid meniscus inside the nozzle, just prior to filament pinch-off, can be observed in order to gauge the effect of the driving condition. The meniscus motion for three different solution concentrations, at the same driving condition, are shown in figure 3 (and supplementary movie 3). A detailed description of such motion, and how it is affected by changing the driving conditions, can be found in Fraters et al. (Reference Fraters2021). The position of the meniscus, ![]() $z_{m}$, is tracked as shown in figure 3(a), and its temporal evolution is plotted in figure 3(d). From figure 3(d), it is observed that the maximum meniscus position,
$z_{m}$, is tracked as shown in figure 3(a), and its temporal evolution is plotted in figure 3(d). From figure 3(d), it is observed that the maximum meniscus position, ![]() $z_{m, max}$, is the same for the three different solution concentrations. In other words,
$z_{m, max}$, is the same for the three different solution concentrations. In other words, ![]() $z_{m, max}$, is only affected by the pulse amplitude and pulse width (Fraters et al. Reference Fraters2021), and not by the amount of polymer present in the solutions used in the present work. Thus,
$z_{m, max}$, is only affected by the pulse amplitude and pulse width (Fraters et al. Reference Fraters2021), and not by the amount of polymer present in the solutions used in the present work. Thus, ![]() $z_{m, max}$ can be considered to be a suitable variable to represent the effect of the driving conditions. It is non-dimensionalized with the nozzle diameter,
$z_{m, max}$ can be considered to be a suitable variable to represent the effect of the driving conditions. It is non-dimensionalized with the nozzle diameter, ![]() $d_{n}$, as
$d_{n}$, as

Figure 3. Motion of the liquid meniscus inside the nozzle, at ![]() $V_{A, max} = 60$ V,
$V_{A, max} = 60$ V, ![]() $t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s, for (a) 0.001 % PEO1M, (b) 0.003 % PEO1M and (c) 0.009 % PEO1M solutions, basically showing no difference. (d) The variation of the meniscus position (
$t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s, for (a) 0.001 % PEO1M, (b) 0.003 % PEO1M and (c) 0.009 % PEO1M solutions, basically showing no difference. (d) The variation of the meniscus position (![]() $z_{m}$) with time (
$z_{m}$) with time (![]() $t$). For the same driving condition (both
$t$). For the same driving condition (both ![]() $V_{A, max}$,
$V_{A, max}$, ![]() $t_{w}$ kept constant), the maximum meniscus position (
$t_{w}$ kept constant), the maximum meniscus position (![]() $z_{m, max}$) is independent of the polymer concentration. The dashed lines are guides for the eyes.
$z_{m, max}$) is independent of the polymer concentration. The dashed lines are guides for the eyes.
The second dimensionless parameter for the two-dimensional parameter space must be related to the composition of the jetted liquid. The solution concentration is associated with its relaxation time, ![]() $\lambda$. With increasing polymer concentration,
$\lambda$. With increasing polymer concentration, ![]() $\lambda$ increases (Deblais et al. Reference Deblais, Velikov and Bonn2018, Reference Deblais, Herrada, Eggers and Bonn2020). The relaxation time is non-dimensionalized with the capillary time, resulting in the nozzle Deborah number,
$\lambda$ increases (Deblais et al. Reference Deblais, Velikov and Bonn2018, Reference Deblais, Herrada, Eggers and Bonn2020). The relaxation time is non-dimensionalized with the capillary time, resulting in the nozzle Deborah number, ![]() $De_{n}$, defined as
$De_{n}$, defined as
with
 \begin{equation} t_{\gamma, n} = \left( \frac{\rho d_{n}^{3}}{8 \gamma} \right)^{1/2}, \end{equation}
\begin{equation} t_{\gamma, n} = \left( \frac{\rho d_{n}^{3}}{8 \gamma} \right)^{1/2}, \end{equation}
where ![]() $\rho$ is the density of the fluid and
$\rho$ is the density of the fluid and ![]() $\gamma$ is the surface tension.
$\gamma$ is the surface tension.
The regime map in the ![]() $\tilde {z}_{m}$–
$\tilde {z}_{m}$–![]() $De_{n}$ parameter space is shown in figure 4. As expected from the observations made in figure 2, the desirable ‘no satellite’ (green markers) regime lies in the middle of the phase space, flanked by the ‘satellite’ (blue markers) and ‘no jetting’ (red markers) regimes. For a particular polymer concentration (constant
$De_{n}$ parameter space is shown in figure 4. As expected from the observations made in figure 2, the desirable ‘no satellite’ (green markers) regime lies in the middle of the phase space, flanked by the ‘satellite’ (blue markers) and ‘no jetting’ (red markers) regimes. For a particular polymer concentration (constant ![]() $De_{n}$), a stronger driving (higher
$De_{n}$), a stronger driving (higher ![]() $\tilde {z}_{m}$) is required to overcome the elastic effects and traverse from the ‘no jetting’ regime to the ‘no satellite’ regime. However, if the driving is too strong, the stabilizing effect of elasticity on the retracting tail is lost, resulting in the tail to break, forming satellites.
$\tilde {z}_{m}$) is required to overcome the elastic effects and traverse from the ‘no jetting’ regime to the ‘no satellite’ regime. However, if the driving is too strong, the stabilizing effect of elasticity on the retracting tail is lost, resulting in the tail to break, forming satellites.

Figure 4. Regime map based on the nozzle Deborah number (![]() $De_{n}$) and the non-dimensional maximum meniscus position (
$De_{n}$) and the non-dimensional maximum meniscus position (![]() $\tilde {z}_{m}$). The insets show the typical jetting (or lack of) behaviour observed in each regime, namely satellite formation (blue markers) for low
$\tilde {z}_{m}$). The insets show the typical jetting (or lack of) behaviour observed in each regime, namely satellite formation (blue markers) for low ![]() $De_{n}$ and high
$De_{n}$ and high ![]() $\tilde {z}_{m}$, no satellite formation (green markers) for intermediate
$\tilde {z}_{m}$, no satellite formation (green markers) for intermediate ![]() $De_{n}$ and
$De_{n}$ and ![]() $\tilde {z}_{m}$, and no jetting (red markers) for high
$\tilde {z}_{m}$, and no jetting (red markers) for high ![]() $De_{n}$ and low
$De_{n}$ and low ![]() $\tilde {z}_{m}$. Each datapoint represents approximately 25 experiments.
$\tilde {z}_{m}$. Each datapoint represents approximately 25 experiments.
4. Filament retraction: experiments
The instantaneous retraction length, ![]() $L(t)$, is measured between the extremities of the head droplet and the tail droplet, as shown in the inset of figure 5. The temporal evolution of
$L(t)$, is measured between the extremities of the head droplet and the tail droplet, as shown in the inset of figure 5. The temporal evolution of ![]() $L(t)$ is plotted in figure 5(a) for different solution concentrations (
$L(t)$ is plotted in figure 5(a) for different solution concentrations (![]() $De_{n}$) and driving conditions (
$De_{n}$) and driving conditions (![]() $\tilde {z}_{m}$). The retraction length appears to decrease linearly with time even for the viscoelastic liquids (
$\tilde {z}_{m}$). The retraction length appears to decrease linearly with time even for the viscoelastic liquids (![]() $De_{n} \neq 0$) (dashed lines in figure 5a); a trend that is expected for Newtonian liquids (
$De_{n} \neq 0$) (dashed lines in figure 5a); a trend that is expected for Newtonian liquids (![]() $De_{n} \simeq 0$) (Planchette et al. Reference Planchette, Marangon, Hsiao and Brenn2019). The retraction velocity that is extracted from the slopes of these curves is approximately constant in time for each dataset shown in figure 5(a), but different from that of a Newtonian filament (see figure 5a), where it is equal to the Taylor–Culick velocity (Keller Reference Keller1983; Hoepffner & Paré Reference Hoepffner and Paré2013; Pierson et al. Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020)
$De_{n} \simeq 0$) (Planchette et al. Reference Planchette, Marangon, Hsiao and Brenn2019). The retraction velocity that is extracted from the slopes of these curves is approximately constant in time for each dataset shown in figure 5(a), but different from that of a Newtonian filament (see figure 5a), where it is equal to the Taylor–Culick velocity (Keller Reference Keller1983; Hoepffner & Paré Reference Hoepffner and Paré2013; Pierson et al. Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020)
 \begin{equation} v_{TC} = \left( \frac{\gamma}{\rho R_{0}} \right)^{1/2}, \end{equation}
\begin{equation} v_{TC} = \left( \frac{\gamma}{\rho R_{0}} \right)^{1/2}, \end{equation}
where ![]() $R_{0}$ is the radius of the retracting filament. In the present experiments,
$R_{0}$ is the radius of the retracting filament. In the present experiments, ![]() $R_{0}$ is measured at a location on the contracting filament close to the head droplet, and at a time instant
$R_{0}$ is measured at a location on the contracting filament close to the head droplet, and at a time instant ![]() $t = t_{0}$ after pinch-off from the nozzle. In certain experiments, post pinch-off, spurious effects such as out-of-plane oscillations were observed. These were adjudged to be initial transients, and removed from the datasets plotted in figure 5(a). The value of
$t = t_{0}$ after pinch-off from the nozzle. In certain experiments, post pinch-off, spurious effects such as out-of-plane oscillations were observed. These were adjudged to be initial transients, and removed from the datasets plotted in figure 5(a). The value of ![]() $t_{0}$ thus corresponds to the first datapoint of each dataset in figure 5(a). The error bars in figure 5 represent
$t_{0}$ thus corresponds to the first datapoint of each dataset in figure 5(a). The error bars in figure 5 represent ![]() $\pm$ one standard deviation across approximately 25 experiments for each dataset. The ratio of the retraction velocities (
$\pm$ one standard deviation across approximately 25 experiments for each dataset. The ratio of the retraction velocities (![]() $v_{ret}$) of the viscoelastic filaments in the current experiments (measured from the linear fits in figure 5a) to the corresponding Newtonian Taylor–Culick velocity (
$v_{ret}$) of the viscoelastic filaments in the current experiments (measured from the linear fits in figure 5a) to the corresponding Newtonian Taylor–Culick velocity (![]() $v_{TC}$) is plotted in figure 5(b) against the filament Deborah number, defined as
$v_{TC}$) is plotted in figure 5(b) against the filament Deborah number, defined as
where
 \begin{equation} t_{\gamma} = \left( \frac{\rho R_{0}^{3}}{\gamma} \right)^{1/2}. \end{equation}
\begin{equation} t_{\gamma} = \left( \frac{\rho R_{0}^{3}}{\gamma} \right)^{1/2}. \end{equation}
In the present experiments, ![]() $De_{0} /De_{n} \sim O(10)$. Furthermore,
$De_{0} /De_{n} \sim O(10)$. Furthermore, ![]() $R_{0}$ was observed to vary over a very narrow range (4–13
$R_{0}$ was observed to vary over a very narrow range (4–13 ![]() $\mathrm {\mu }$m) in the present experiments, resulting in more than one
$\mathrm {\mu }$m) in the present experiments, resulting in more than one ![]() $De_{0}$ value in some cases for a given
$De_{0}$ value in some cases for a given ![]() $De_{n}$. Figure 5(b) shows that the viscoelastic filaments have a higher retraction velocity than the Newtonian ones. Moreover, it can be observed from figure 5(b) that for the same
$De_{n}$. Figure 5(b) shows that the viscoelastic filaments have a higher retraction velocity than the Newtonian ones. Moreover, it can be observed from figure 5(b) that for the same ![]() $De_{0}$, there are more than one
$De_{0}$, there are more than one ![]() $v_{ret}$ value. This suggests that the relaxation time,
$v_{ret}$ value. This suggests that the relaxation time, ![]() $\lambda$, is not the only parameter affecting the retraction of these filaments; the retraction is also affected by the driving conditions at which the solution is jetted. To characterize the effect of the driving conditions on
$\lambda$, is not the only parameter affecting the retraction of these filaments; the retraction is also affected by the driving conditions at which the solution is jetted. To characterize the effect of the driving conditions on ![]() $v_{ret}$, we plot
$v_{ret}$, we plot ![]() $v_{ret}/v_{TC}$ as a function of
$v_{ret}/v_{TC}$ as a function of ![]() $\tilde {z}_{m}$ for different
$\tilde {z}_{m}$ for different ![]() $De_{n}$ in figure 5(c). However, no clear trend is observed in the plot. This is probably due to the complex flow profile associated with the motion of the meniscus, and is essentially a limitation of the experimental set-up.
$De_{n}$ in figure 5(c). However, no clear trend is observed in the plot. This is probably due to the complex flow profile associated with the motion of the meniscus, and is essentially a limitation of the experimental set-up.

Figure 5. (a) Temporal evolution of the length ![]() $L(t)$ of the travelling liquid filaments with time
$L(t)$ of the travelling liquid filaments with time ![]() $t$. The inset shows a typical measurement. The dashed lines are linear fits. (b) Variation of the ratio of the filament retraction velocity (
$t$. The inset shows a typical measurement. The dashed lines are linear fits. (b) Variation of the ratio of the filament retraction velocity (![]() $v_{ret}$, measured from the experiments) to the corresponding Newtonian Taylor–Culick velocity (
$v_{ret}$, measured from the experiments) to the corresponding Newtonian Taylor–Culick velocity (![]() $v_{TC}$), plotted against the filament Deborah number,
$v_{TC}$), plotted against the filament Deborah number, ![]() $De_{0}$. The dashed line indicates the Newtonian behaviour,
$De_{0}$. The dashed line indicates the Newtonian behaviour, ![]() $v_{ret} = v_{TC}$. (c) Variation of
$v_{ret} = v_{TC}$. (c) Variation of ![]() $v_{ret}/v_{TC}$ plotted against the maximum meniscus position (
$v_{ret}/v_{TC}$ plotted against the maximum meniscus position (![]() $\tilde {z}_{m}$). The dashed line indicates Newtonian behaviour,
$\tilde {z}_{m}$). The dashed line indicates Newtonian behaviour, ![]() $v_{ret} = v_{TC}$.
$v_{ret} = v_{TC}$.
5. Filament retraction: theoretical model
In order to identify the role of viscoelasticity in the retraction velocity of liquid filaments, a simplified theoretical model is proposed. The retraction dynamics of viscoelastic liquid films has been studied in other geometries (Evers, Shulepov & Frens Reference Evers, Shulepov and Frens1997; Dalnoki-Veress et al. Reference Dalnoki-Veress, Nickel, Roth and Dutcher1999; Villone et al. Reference Villone, D'Avino, Di Maio, Hulsen and Maffettone2017; Tammaro et al. Reference Tammaro, Pasquino, Villone, D'Avino, Ferraro, Di Maio, Langella, Grizzuti and Maffettone2018; Villone, Hulsen & Maffettone Reference Villone, Hulsen and Maffettone2019), but not for a slender liquid filament. We follow the lines of Pierson et al. (Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020) for Newtonian liquid filaments, but now account for the viscoelasticity due to the polymers. A careful examination of the retraction phenomenon (figure 6a) reveals that, during the retraction, the size of the head droplet does not change noticeably (<3 %), while the slender tail is pulled towards the head droplet. During this retraction, the spherical tail droplet grows in size as the tail length decreases. This behaviour is modelled by the geometry shown in figure 6(b).

Figure 6. (a) The evolution of a jetted 0.005 % PEO1M ligament produced at ![]() $V_{A, max} = 60$ V,
$V_{A, max} = 60$ V, ![]() $t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s. (b) Schematic of the geometry for the theoretical model, also clarifying the employed notation.
$t_{w} = 40\,\mathrm {\mu }$s. (b) Schematic of the geometry for the theoretical model, also clarifying the employed notation.
At time ![]() $t = t_{0}$, the tail in figure 6(a) is modelled as a long cylindrical filament with a rounded end (shown by the black dashed lines in figure 6b), having radius
$t = t_{0}$, the tail in figure 6(a) is modelled as a long cylindrical filament with a rounded end (shown by the black dashed lines in figure 6b), having radius ![]() $R_{0}$ and length
$R_{0}$ and length ![]() $L_{0}$. We consider an axisymmetric coordinate system that is co-moving with the head droplet (the head droplet moves with a constant velocity in the present experiments), which implies that the fluid within the tail is initially at rest in this coordinate system. One can then proceed via a momentum balance over the control volume that is indicated by the red dashed rectangle. The surface and elastic tensions pull the filament towards the head droplet. For
$L_{0}$. We consider an axisymmetric coordinate system that is co-moving with the head droplet (the head droplet moves with a constant velocity in the present experiments), which implies that the fluid within the tail is initially at rest in this coordinate system. One can then proceed via a momentum balance over the control volume that is indicated by the red dashed rectangle. The surface and elastic tensions pull the filament towards the head droplet. For ![]() $t > t_{0}$, the rounded edge of the filament therefore starts to retract in the negative
$t > t_{0}$, the rounded edge of the filament therefore starts to retract in the negative ![]() $z$-direction, with an instantaneous length
$z$-direction, with an instantaneous length ![]() $L(t)$. As the tail retracts, liquid from the tail feeds the tail droplet (Savva & Bush Reference Savva and Bush2009; Pierson et al. Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020), resulting in an increase of its size. Below, we will use the fact that most of the liquid momentum is localized inside the tail droplet, as it moves inwards with an instantaneous velocity
$L(t)$. As the tail retracts, liquid from the tail feeds the tail droplet (Savva & Bush Reference Savva and Bush2009; Pierson et al. Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020), resulting in an increase of its size. Below, we will use the fact that most of the liquid momentum is localized inside the tail droplet, as it moves inwards with an instantaneous velocity ![]() ${\textrm {d}}L/{\textrm {d}}t$. Note that
${\textrm {d}}L/{\textrm {d}}t$. Note that ![]() $L(t)$ is defined slightly differently to the definition used in the experimental data. However, since the diameter of the head droplet does not change appreciably, the following analysis holds well for describing the retraction.
$L(t)$ is defined slightly differently to the definition used in the experimental data. However, since the diameter of the head droplet does not change appreciably, the following analysis holds well for describing the retraction.
We formalize these ideas using the slender jet approximation (![]() $R_{0} \ll L$), within that the mass and momentum conservations can be written as (Eggers Reference Eggers1993; Eggers & Dupont Reference Eggers and Dupont1994; Shi, Brenner & Nagel Reference Shi, Brenner and Nagel1994; Clasen et al. Reference Clasen, Eggers, Fontelos, Li and McKinley2006a)
$R_{0} \ll L$), within that the mass and momentum conservations can be written as (Eggers Reference Eggers1993; Eggers & Dupont Reference Eggers and Dupont1994; Shi, Brenner & Nagel Reference Shi, Brenner and Nagel1994; Clasen et al. Reference Clasen, Eggers, Fontelos, Li and McKinley2006a)
and
Here, ![]() $v(z,t)$ and
$v(z,t)$ and ![]() $r(z,t)$, respectively are the axial velocity and the filament radius, prime denotes a derivative along
$r(z,t)$, respectively are the axial velocity and the filament radius, prime denotes a derivative along ![]() $z$, while
$z$, while ![]() $\eta _{s}$ is the solvent viscosity, and
$\eta _{s}$ is the solvent viscosity, and ![]() $\kappa$ is the curvature of the filament, given by
$\kappa$ is the curvature of the filament, given by
The viscoelasticity is accounted for by ![]() $\sigma _{zz}$ and
$\sigma _{zz}$ and ![]() $\sigma _{rr}$, the components of the polymer stress tensor
$\sigma _{rr}$, the components of the polymer stress tensor ![]() $\boldsymbol {\sigma }$, for which a separate constitutive equation needs to be specified (Bird et al. Reference Bird, Curtiss, Armstrong and Hassager1987). In the slender jet geometry, the predominant stretching and viscoelastic contribution is along the
$\boldsymbol {\sigma }$, for which a separate constitutive equation needs to be specified (Bird et al. Reference Bird, Curtiss, Armstrong and Hassager1987). In the slender jet geometry, the predominant stretching and viscoelastic contribution is along the ![]() $z$-direction, so
$z$-direction, so ![]() $\sigma _{rr}$ can be omitted in the remainder (Clasen et al. Reference Clasen, Eggers, Fontelos, Li and McKinley2006a; Eggers & Fontelos Reference Eggers and Fontelos2015).
$\sigma _{rr}$ can be omitted in the remainder (Clasen et al. Reference Clasen, Eggers, Fontelos, Li and McKinley2006a; Eggers & Fontelos Reference Eggers and Fontelos2015).
In order to perform the control volume analysis, one can bring the slender jet equations to a conservative form by multiplying (5.1) by ![]() $\rho v$ and (5.2) by
$\rho v$ and (5.2) by ![]() $r^{2}$, and then adding them up to obtain (Clasen et al. Reference Clasen, Eggers, Fontelos, Li and McKinley2006a; Eggers & Villermaux Reference Eggers and Villermaux2008)
$r^{2}$, and then adding them up to obtain (Clasen et al. Reference Clasen, Eggers, Fontelos, Li and McKinley2006a; Eggers & Villermaux Reference Eggers and Villermaux2008)
where
The right-hand side of (5.4) can readily be integrated from ![]() $z=0$ to
$z=0$ to ![]() $z=L(t)$, over the control volume in figure 6(b). We integrate the equation using the same assumptions as in Pierson et al. (Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020): (i)
$z=L(t)$, over the control volume in figure 6(b). We integrate the equation using the same assumptions as in Pierson et al. (Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020): (i) ![]() $r$ vanishes at
$r$ vanishes at ![]() $z = L(t)$, as that is the tip of the filament; (ii) the filament radius is uniform (
$z = L(t)$, as that is the tip of the filament; (ii) the filament radius is uniform (![]() $r=R_0$ and
$r=R_0$ and ![]() $r'=0$) at
$r'=0$) at ![]() $z = 0$, which is at an arbitrary location close to the head droplet; (iii) the fluid is at rest (
$z = 0$, which is at an arbitrary location close to the head droplet; (iii) the fluid is at rest (![]() $v=v'=0$) at
$v=v'=0$) at ![]() $z = 0$. Defining the total momentum
$z = 0$. Defining the total momentum ![]() $P = {\rm \pi}\rho \int _{0}^{L(t)} r^{2} v\,{\textrm {d}}z$, we can then indeed integrate (5.4) from
$P = {\rm \pi}\rho \int _{0}^{L(t)} r^{2} v\,{\textrm {d}}z$, we can then indeed integrate (5.4) from ![]() $z = 0$ to
$z = 0$ to ![]() $z = L(t)$ as Savva & Bush (Reference Savva and Bush2009) and Pierson et al. (Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020)
$z = L(t)$ as Savva & Bush (Reference Savva and Bush2009) and Pierson et al. (Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020)
We recover the anticipated momentum balance, with capillary and elastic forces pulling the liquid tail towards the head drop.
Now, the retraction process is feeding the tail droplet (Savva & Bush Reference Savva and Bush2009; Pierson et al. Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020), while the fluid between the head and the tail droplets remains at rest (Pierson et al. Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020). Therefore, ![]() $P$ is essentially the momentum of the tail droplet
$P$ is essentially the momentum of the tail droplet ![]() $P = M_T \,{\textrm {d}}L/{\textrm {d}}t$ (assuming that the fluid velocity inside the droplet is constant, Pierson et al. Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020). The mass
$P = M_T \,{\textrm {d}}L/{\textrm {d}}t$ (assuming that the fluid velocity inside the droplet is constant, Pierson et al. Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020). The mass ![]() $M_T(t)$ of the tail drop increases over time by the mass flow rate
$M_T(t)$ of the tail drop increases over time by the mass flow rate ![]() $- {\rm \pi}\rho R_{0}^{2} \,{\textrm {d}}L/{\textrm {d}}t$, such that
$- {\rm \pi}\rho R_{0}^{2} \,{\textrm {d}}L/{\textrm {d}}t$, such that
In the analysis that follows, we omit the initial mass (![]() $2 {\rm \pi}\rho R_{0}^{3}/3$) of the edge of the filament (Pierson et al. Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020), which is negligible in the experimental data with which we compare our theoretical calculations. Integration of (5.6) in time then gives
$2 {\rm \pi}\rho R_{0}^{3}/3$) of the edge of the filament (Pierson et al. Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020), which is negligible in the experimental data with which we compare our theoretical calculations. Integration of (5.6) in time then gives
 \begin{equation} P = {\rm \pi}\rho R_0^{2} (L_0-L)\frac{{\textrm{d}}L}{{\textrm{d}}T} ={-} {\rm \pi}\left(\gamma R_{0}T + R_{0}^{2} \int_0^\textrm{T} \sigma_{zz}(\bar t) \vert_{z=0} \,{\textrm{d}}\bar t \right), \end{equation}
\begin{equation} P = {\rm \pi}\rho R_0^{2} (L_0-L)\frac{{\textrm{d}}L}{{\textrm{d}}T} ={-} {\rm \pi}\left(\gamma R_{0}T + R_{0}^{2} \int_0^\textrm{T} \sigma_{zz}(\bar t) \vert_{z=0} \,{\textrm{d}}\bar t \right), \end{equation}
where we have introduced a change of variable with ![]() $T = t- t_{0}$. For a Newtonian fluid (
$T = t- t_{0}$. For a Newtonian fluid (![]() $\sigma _{zz}=0$), this equation can be integrated to
$\sigma _{zz}=0$), this equation can be integrated to ![]() $(L_0-L)^{2} = ({\gamma }/{\rho R_0})T^{2}$ and one recovers a retraction with a constant (Taylor–Culick) velocity (Keller Reference Keller1983; Hoepffner & Paré Reference Hoepffner and Paré2013; Pierson et al. Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020). It is clear that the presence of elastic stress will offer an extra contribution that speeds up the retraction, as observed in experiments. Importantly, however, the relaxation of
$(L_0-L)^{2} = ({\gamma }/{\rho R_0})T^{2}$ and one recovers a retraction with a constant (Taylor–Culick) velocity (Keller Reference Keller1983; Hoepffner & Paré Reference Hoepffner and Paré2013; Pierson et al. Reference Pierson, Magnaudet, Soares and Popinet2020). It is clear that the presence of elastic stress will offer an extra contribution that speeds up the retraction, as observed in experiments. Importantly, however, the relaxation of ![]() $\sigma _{zz}(T)$ will lead to a nonlinear evolution of
$\sigma _{zz}(T)$ will lead to a nonlinear evolution of ![]() $L(T)$, so that the retraction velocity is no longer constant.
$L(T)$, so that the retraction velocity is no longer constant.
To close the problem, we need a constitutive relation for the polymeric stress. Here we use the Oldroyd-B fluid that has been successfully used to describe the thinning of jets (Clasen et al. Reference Clasen, Eggers, Fontelos, Li and McKinley2006a; Eggers et al. Reference Eggers, Herrada and Snoeijer2020). In terms of the conformation tensor ![]() $\boldsymbol{\mathsf{A}}$, the stress is then given by a constitutive relation (Bird et al. Reference Bird, Curtiss, Armstrong and Hassager1987)
$\boldsymbol{\mathsf{A}}$, the stress is then given by a constitutive relation (Bird et al. Reference Bird, Curtiss, Armstrong and Hassager1987)
where ![]() $\eta _p$ is the polymer viscosity. In the Oldroyd-B fluid, the conformation tensor evolves by a linear relaxation dynamics, which in the slender jet approximation reads (Fontelos & Li Reference Fontelos and Li2004)
$\eta _p$ is the polymer viscosity. In the Oldroyd-B fluid, the conformation tensor evolves by a linear relaxation dynamics, which in the slender jet approximation reads (Fontelos & Li Reference Fontelos and Li2004)
Using the same assumptions used for deriving (5.6) and using that ![]() $A_{zz} \gg 1$ (large stretching of polymer chains along the axis), (5.10) can be reduced to
$A_{zz} \gg 1$ (large stretching of polymer chains along the axis), (5.10) can be reduced to
The polymer stress then follows as
The initial condition ![]() $A_0=A_{zz}(z=0,\ T=0)$ is not determined from the present analysis, but is an inherited condition from the jetting phase, where the polymers are deformed by the stretching flow.
$A_0=A_{zz}(z=0,\ T=0)$ is not determined from the present analysis, but is an inherited condition from the jetting phase, where the polymers are deformed by the stretching flow.
We now return to (5.8) with the polymer stress given by (5.12), so that
This can be integrated with the initial condition ![]() $L(0) = L_{0}$, to yield the variation of the retracting length with time, given by
$L(0) = L_{0}$, to yield the variation of the retracting length with time, given by
This is the central result of the analysis. Although the resulting ![]() $L(T)$ is nonlinear, the variation of
$L(T)$ is nonlinear, the variation of ![]() $L$ with
$L$ with ![]() $T$ appears nearly linear (see result plotted in figure 7a). To highlight the effect of viscoelasticity, the corresponding Newtonian Taylor–Culick prediction for each dataset is also shown in figure 7(a) by dashed lines. It can be clearly observed from figure 7(a) that viscoelastic retraction (discrete datapoints from experiments and solid lines from fitting (5.14)) is faster than the corresponding Newtonian Taylor–Culick retraction. Given the nearly linear appearance of
$T$ appears nearly linear (see result plotted in figure 7a). To highlight the effect of viscoelasticity, the corresponding Newtonian Taylor–Culick prediction for each dataset is also shown in figure 7(a) by dashed lines. It can be clearly observed from figure 7(a) that viscoelastic retraction (discrete datapoints from experiments and solid lines from fitting (5.14)) is faster than the corresponding Newtonian Taylor–Culick retraction. Given the nearly linear appearance of ![]() $L(T)$, it is therefore instructive to expand (5.14) for early times
$L(T)$, it is therefore instructive to expand (5.14) for early times ![]() $T/\lambda \ll 1$, which gives
$T/\lambda \ll 1$, which gives
This illustrates the enhanced contraction velocity ![]() $(v_{TC}^{2} + {\eta _{p} A_{0}}/{\lambda \rho })^{1/2}$ during the initial stage. A result of this form can be obtained even more generally, beyond the assumptions underlying the Oldroyd-B fluid. Namely, evaluating the stress integral at short time in (5.8), one finds the initial retraction velocity
$(v_{TC}^{2} + {\eta _{p} A_{0}}/{\lambda \rho })^{1/2}$ during the initial stage. A result of this form can be obtained even more generally, beyond the assumptions underlying the Oldroyd-B fluid. Namely, evaluating the stress integral at short time in (5.8), one finds the initial retraction velocity
 \begin{equation} v_{ret} = \left(v_{TC}^{2} + \frac{\sigma_{zz}(z=0, T=0)}{\rho} \right)^{1/2}, \end{equation}
\begin{equation} v_{ret} = \left(v_{TC}^{2} + \frac{\sigma_{zz}(z=0, T=0)}{\rho} \right)^{1/2}, \end{equation}incremented by the elastic stress that is initially in the filament.

Figure 7. Filament length ![]() $L(t)$ as a function of time: (a) fitting of the theoretical predictions (solid lines) with experimental observations (discrete datapoints); the dashed lines indicate the corresponding Newtonian (Taylor–Culick) behaviour. (b) Linear behaviour at small
$L(t)$ as a function of time: (a) fitting of the theoretical predictions (solid lines) with experimental observations (discrete datapoints); the dashed lines indicate the corresponding Newtonian (Taylor–Culick) behaviour. (b) Linear behaviour at small ![]() $T/\lambda$ as predicted by (5.17); the discrete datapoints correspond to the experiments while the solid lines indicate the prediction from (5.17) valid for small times
$T/\lambda$ as predicted by (5.17); the discrete datapoints correspond to the experiments while the solid lines indicate the prediction from (5.17) valid for small times ![]() $T/\lambda < 1$. (c) Variation of the fitted
$T/\lambda < 1$. (c) Variation of the fitted ![]() $A_{0}^{1/2}$ with the initial aspect ratio (
$A_{0}^{1/2}$ with the initial aspect ratio (![]() $L_{0}/R_{0}$). The dashed line representing a linear fit. (d) Variation of
$L_{0}/R_{0}$). The dashed line representing a linear fit. (d) Variation of ![]() $A_{0}^{1/2}$ with
$A_{0}^{1/2}$ with ![]() $De_{0}$.
$De_{0}$.
Finally, one may use (5.14) to estimate ![]() $A_{0}$ in our experiments, which is otherwise difficult a priori. The fitting was performed by matching
$A_{0}$ in our experiments, which is otherwise difficult a priori. The fitting was performed by matching ![]() $L_{0}$ (at
$L_{0}$ (at ![]() $T = 0$) and
$T = 0$) and ![]() $L$ from the experiments at the final
$L$ from the experiments at the final ![]() $T$ instant for each dataset, as shown in figure 7(a) by the continuous lines. We rewrite (5.15) as
$T$ instant for each dataset, as shown in figure 7(a) by the continuous lines. We rewrite (5.15) as
 \begin{equation} \left(\frac{\rho}{\lambda \eta_{p}} \left( \left( L - L_{0} \right)^{2} - \frac{\gamma}{\rho R_{0}} T^{2} \right) \right)^{1/2} = A_{0}^{1/2} \frac{T}{\lambda}. \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \left(\frac{\rho}{\lambda \eta_{p}} \left( \left( L - L_{0} \right)^{2} - \frac{\gamma}{\rho R_{0}} T^{2} \right) \right)^{1/2} = A_{0}^{1/2} \frac{T}{\lambda}. \end{equation}
When plotting the left-hand side of (5.17), expressed as ![]() $\psi$, against
$\psi$, against ![]() $T/\lambda$, a straight line through (0,0) is expected at small values of
$T/\lambda$, a straight line through (0,0) is expected at small values of ![]() $T/\lambda$, with the slope depicting
$T/\lambda$, with the slope depicting ![]() $A_{0}^{1/2}$. This is observed in figure 7(b) for the experimental data (discrete datapoints), with deviations from linear behaviour (continuous lines) observed at larger
$A_{0}^{1/2}$. This is observed in figure 7(b) for the experimental data (discrete datapoints), with deviations from linear behaviour (continuous lines) observed at larger ![]() $T/\lambda$ values.
$T/\lambda$ values.
Now, ![]() $A_{0}=A_{zz}\ (z=0,\ T=0)$ is the axial component of the conformation tensor
$A_{0}=A_{zz}\ (z=0,\ T=0)$ is the axial component of the conformation tensor ![]() $\boldsymbol{\mathsf{A}}$, which itself is defined as
$\boldsymbol{\mathsf{A}}$, which itself is defined as ![]() $\boldsymbol{\mathsf{A}} = \langle \boldsymbol {X} \boldsymbol {X} \rangle /X_{e}^{2}$ (Bird et al. Reference Bird, Curtiss, Armstrong and Hassager1987), where
$\boldsymbol{\mathsf{A}} = \langle \boldsymbol {X} \boldsymbol {X} \rangle /X_{e}^{2}$ (Bird et al. Reference Bird, Curtiss, Armstrong and Hassager1987), where ![]() $\boldsymbol {X}$ is the stretched length of each individual polymer molecule, and
$\boldsymbol {X}$ is the stretched length of each individual polymer molecule, and ![]() $X_{e}$ its equilibrium length. Here, the polymer molecules are pictured to be two spherical beads connected by a spring. Therefore, one can argue that
$X_{e}$ its equilibrium length. Here, the polymer molecules are pictured to be two spherical beads connected by a spring. Therefore, one can argue that ![]() $A_{0}^{1/2}$ is proportional to the stretched length of the polymer molecules at
$A_{0}^{1/2}$ is proportional to the stretched length of the polymer molecules at ![]() $t = t_{0}$ (or
$t = t_{0}$ (or ![]() $T = 0$) and
$T = 0$) and ![]() $z = 0$. The stretched length of the polymer is proportional to the local polymer stretching,
$z = 0$. The stretched length of the polymer is proportional to the local polymer stretching, ![]() $\epsilon _{l}$, while the initial aspect ratio,
$\epsilon _{l}$, while the initial aspect ratio, ![]() $L_{0}/R_{0}$, of the filament may be proportional to the stretching of the filament,
$L_{0}/R_{0}$, of the filament may be proportional to the stretching of the filament, ![]() $\epsilon _{g}$. It may be expected that
$\epsilon _{g}$. It may be expected that ![]() $\epsilon _{l}$ and
$\epsilon _{l}$ and ![]() $\epsilon _{g}$ are correlated under strong axial tension for a slender liquid filament. Hence,
$\epsilon _{g}$ are correlated under strong axial tension for a slender liquid filament. Hence, ![]() $A_{0}^{1/2}$ can be assumed to be linearly correlated to
$A_{0}^{1/2}$ can be assumed to be linearly correlated to ![]() $L_{0}/R_{0}$. The variation of
$L_{0}/R_{0}$. The variation of ![]() $A_{0}^{1/2}$ with
$A_{0}^{1/2}$ with ![]() $L_{0}/R_{0}$ is plotted in figure 7(c); the dependence is not inconsistent with the assumed linear behaviour. The values of
$L_{0}/R_{0}$ is plotted in figure 7(c); the dependence is not inconsistent with the assumed linear behaviour. The values of ![]() $A_{0}^{1/2}$ obtained from fitting with the experiments are
$A_{0}^{1/2}$ obtained from fitting with the experiments are ![]() $O(100)$, and one may wonder whether the finite extensibility of polymers (ignored in the Oldroyd-B model) may play a role. Determining the finite extensibility from rheological experiments is a challenge. Lindner, Vermant & Bonn (Reference Lindner, Vermant and Bonn2003) report, for higher molecular weight PEO (
$O(100)$, and one may wonder whether the finite extensibility of polymers (ignored in the Oldroyd-B model) may play a role. Determining the finite extensibility from rheological experiments is a challenge. Lindner, Vermant & Bonn (Reference Lindner, Vermant and Bonn2003) report, for higher molecular weight PEO (![]() $2 \times 10^{6}$ and
$2 \times 10^{6}$ and ![]() $4\times 10^{6}$ a.u.), maximum polymer stretched lengths in the range of
$4\times 10^{6}$ a.u.), maximum polymer stretched lengths in the range of ![]() $O(10)$ to
$O(10)$ to ![]() $O(100)$. The deviations in
$O(100)$. The deviations in ![]() $A_{0}^{1/2}$ from the assumed linear trend might therefore be attributed to the limitations of the Oldroyd-B model. We remark, however, that any analysis with nonlinear constitutive relations will come with additional (unknown) fitting parameters. In addition, there are other factors that may play a role in the retraction dynamics such as polydispersity and multiple relaxation time scales of the polymer molecular chains (Entov & Hinch Reference Entov and Hinch1997; Wagner et al. Reference Wagner, Amarouchene, Bonn and Eggers2005), a non-uniform radius of the filament along the axial direction, non-axisymmetric effects at the nozzle exit (van der Meulen et al. Reference van der Meulen, Reinten, Wijshoff, Versluis, Lohse and Steen2020) and wetting effects at the nozzle exit (Beulen et al. Reference Beulen, de Jong, Reinten, van der Berg, Wijshoff and van Dongen2007; de Jong et al. Reference de Jong, Reinten, Wijshoff, van der Berg, Delescen, van Dongen, Mugele, Versluis and Lohse2007), which we have not considered in the present study. Figure 7(c) also suggests that
$A_{0}^{1/2}$ from the assumed linear trend might therefore be attributed to the limitations of the Oldroyd-B model. We remark, however, that any analysis with nonlinear constitutive relations will come with additional (unknown) fitting parameters. In addition, there are other factors that may play a role in the retraction dynamics such as polydispersity and multiple relaxation time scales of the polymer molecular chains (Entov & Hinch Reference Entov and Hinch1997; Wagner et al. Reference Wagner, Amarouchene, Bonn and Eggers2005), a non-uniform radius of the filament along the axial direction, non-axisymmetric effects at the nozzle exit (van der Meulen et al. Reference van der Meulen, Reinten, Wijshoff, Versluis, Lohse and Steen2020) and wetting effects at the nozzle exit (Beulen et al. Reference Beulen, de Jong, Reinten, van der Berg, Wijshoff and van Dongen2007; de Jong et al. Reference de Jong, Reinten, Wijshoff, van der Berg, Delescen, van Dongen, Mugele, Versluis and Lohse2007), which we have not considered in the present study. Figure 7(c) also suggests that ![]() $A_{0}^{1/2}$ depends on the polymer concentration, which is expected since the higher the polymer concentration, the longer is the relaxation time of the solution, resulting in the ability of the polymers to be stretched longer. Hence, intuitively, one can come to the realization that
$A_{0}^{1/2}$ depends on the polymer concentration, which is expected since the higher the polymer concentration, the longer is the relaxation time of the solution, resulting in the ability of the polymers to be stretched longer. Hence, intuitively, one can come to the realization that ![]() $A_{0}^{1/2}$ increases with the polymer concentration, thus the polymer relaxation time
$A_{0}^{1/2}$ increases with the polymer concentration, thus the polymer relaxation time ![]() $\lambda$, and subsequently
$\lambda$, and subsequently ![]() $De_{0}$. This is also observed in figure 7(d). However, the exact trend for the variation of
$De_{0}$. This is also observed in figure 7(d). However, the exact trend for the variation of ![]() $A_{0}^{1/2}$ with
$A_{0}^{1/2}$ with ![]() $De_{0}$ is rather difficult to predict in the present experiments. We note that this may be due to the complex flow profile associated with the motion of the meniscus (figure 5c), and a simplified approach to estimate the average elongation rate of the polymer macromolecules from the motion of the meniscus itself is unsatisfactory. This can be ascribed to being a limitation of the experimental set-up, and more controlled experiments in a simplified geometry can shed light into the elongation rate of the macromolecules (thus
$De_{0}$ is rather difficult to predict in the present experiments. We note that this may be due to the complex flow profile associated with the motion of the meniscus (figure 5c), and a simplified approach to estimate the average elongation rate of the polymer macromolecules from the motion of the meniscus itself is unsatisfactory. This can be ascribed to being a limitation of the experimental set-up, and more controlled experiments in a simplified geometry can shed light into the elongation rate of the macromolecules (thus ![]() $A_{0}$) prior to the commencement of retraction.
$A_{0}$) prior to the commencement of retraction.
We further clarify the applicability of two of the assumptions used for developing the theoretical model: in the present experiments, the filament radius in figure 6(a) is not uniform but decreases along its distance from the head droplet. However, given the optical resolution of our imaging system, it is extremely difficult to characterize this variation. Hence in the theoretical model in § 5, this variation has not been taken into account. Furthermore, as highlighted by van der Bos et al. (Reference van der Bos, van der Meulen, Driessen, van der Berg, Reinten, Wijshoff, Versluis and Lohse2014), the fluid velocity inside the droplet produced by an inkjet printhead is not constant. However, the primary goal of the present work was to study the retraction of a viscoelastic filament. A simplified model (§ 5) for that purpose was developed, where it was assumed, for simplicity, that the fluid velocity inside the droplet is constant. Despite these aforementioned simplifications, the model was found to describe the experimentally observed retraction speeds being faster than the Newtonian Taylor–Culick velocity reasonably well.
The regime map (figure 4) indicates a transition from the no satellite to satellite regime at low ![]() $De_{n}$ (0–3) and high
$De_{n}$ (0–3) and high ![]() $\tilde {z}_{m}$ (4–6). The exact location of this transition probably can be estimated by comparing the retraction time scale obtained from the theoretical model in the present work with the time scale associated with pinch-off. A starting point for such an analysis could be the recent work by Eggers et al. (Reference Eggers, Herrada and Snoeijer2020). Furthermore, the theoretical model described in the present work is based on the Oldroyd-B model, which cannot capture pinch-off. One would need to consider nonlinear models such as FENE-P to suitably describe pinch-off. Such nonlinear models require additional (unknown) fitting parameters. However, a detailed calculation is beyond the scope of the present work, and has been left as a future exercise.
$\tilde {z}_{m}$ (4–6). The exact location of this transition probably can be estimated by comparing the retraction time scale obtained from the theoretical model in the present work with the time scale associated with pinch-off. A starting point for such an analysis could be the recent work by Eggers et al. (Reference Eggers, Herrada and Snoeijer2020). Furthermore, the theoretical model described in the present work is based on the Oldroyd-B model, which cannot capture pinch-off. One would need to consider nonlinear models such as FENE-P to suitably describe pinch-off. Such nonlinear models require additional (unknown) fitting parameters. However, a detailed calculation is beyond the scope of the present work, and has been left as a future exercise.
6. Conclusions and outlook
The present work demonstrates that adding small amounts of long chain polymers to water-based inks can result in the suppression of satellite droplets formation in inkjet printing. These polymers impart viscoelasticity to the liquid being jetted, resulting in stabilization of the slender finite-length filament against a Rayleigh–Plateau instability. Due to the action of both capillarity and viscoelasticity, the tail droplet is pulled towards the head droplet, while being connected by a thin liquid thread, resulting in the formation of a single droplet without any satellites. However, if the polymer concentration is too high, no droplet is jetted as the increased elasticity prevents pinch-off from the dispensing nozzle. A regime map in terms of the experimental operating parameters was identified, thus delineating the ‘satellite’, ‘no satellite’ and ‘no jetting’ regimes. Moreover, it was observed that, in the ‘no satellite’ regime, the filament essentially retracts linearly with time, with the retraction velocity being higher than the Newtonian Taylor–Culick velocity. A simple theoretical model was developed to derive the retraction velocity for a slender viscoelastic liquid filament, which works reasonably well in modelling the experimental observations. These results are helpful in revealing the complex interplay between inertia, capillarity, and viscoelasticity during the retraction of slender liquid filaments, and are highly useful to predict the behaviour during inkjet printing of polymer solutions.
The novelty of the present work does not lie in demonstrating the suppression of satellite droplets by the addition of polymers. Such suppression behaviour has been shown before (see Christanti & Walker Reference Christanti and Walker2002; Shore & Harrison Reference Shore and Harrison2005; Morrison & Harlen Reference Morrison and Harlen2010; Yan et al. Reference Yan, Carr and Dong2011; Hoath et al. Reference Hoath, Harlen and Hutchings2012, Reference Hoath, Vadillo, Harlen, McIlroy, Morrison, Hsiao, Tuladhar, Jung, Martin and Hutchings2014). However, a quantitative understanding of the physical mechanism for the suppression of satellite droplets by the addition of viscoelasticity to the ink has been lacking in the scientific literature. We attempt to address these knowledge gaps through this present manuscript. Systematic experiments have been performed over a range of polymer concentrations and driving conditions that result in observations ranging from satellite droplets to no satellites and ultimately to the suppression of jetting altogether. To the best of our knowledge, a similar investigation has not been hitherto reported. The retraction behaviour of viscoelastic filaments reported in this manuscript is also new; in particular the higher retraction speeds as compared with the Newtonian Taylor–Culick velocity. Furthermore, the manuscript presents a simplified theoretical model that explains the apparently linear retraction behaviour and shows reasonable agreement with the experimentally observed retraction speeds being faster than the Newtonian Taylor–Culick velocity. Until now there has not yet been such a comparison between experiment and theory, which we provide, though the complexity of the problem unfortunately does not allow for a quantitative one-to-one comparison.
Supplementary material and movies
Supplementary material and movies are available at https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2021.855.
Acknowledgements
U.S. is thankful to M. Jalaal for stimulating discussions, and M. Rump for drawing the schematic of the experimental set-up.
Funding
The support from an Industrial Partnership Programme of the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO), cofinanced by Canon Production Printing B.V., University of Twente, and Eindhoven University of Technology is acknowledged. C.D. and J.H.S. acknowledge support from NWO VICI Grant No. 680-47-632.
Declaration of interests
The authors report no conflict of interest.