Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 August 2016
This work is focused on the modelling of the shear and normal stresses in fibre suspensions that are subjected to a simple shear flow in the presence of short-range lubrication forces, van der Waals and electrostatic forces, as well as solid friction forces between fibres. All of these forces are weighed by the contact probability. The theory is developed for attractive fibres with van der Waals interaction dominating over electrostatic repulsion. The model predicts a simple Bingham law for both the shear stress and the first normal stress difference, with the apparent shear and normal yield stresses proportional to the second and the third power of the particle volume fraction respectively. The model is applied to the experimental data of Rakatekar et al. (Adv. Mater., vol. 21, 2009, pp. 874–878) and Natale et al. (AIChE J., vol. 60, 2014, pp. 1476–1487) on suspensions of carbon nanotubes dispersed in a Newtonian epoxy resin. It reproduces well the quadratic dependence of the apparent yield stress on the particle volume fraction 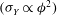 $(\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{Y}\propto \unicode[STIX]{x1D719}^{2})$ for average particle aspect ratios of
$(\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{Y}\propto \unicode[STIX]{x1D719}^{2})$ for average particle aspect ratios of 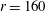 $r=160$ and 1200, while it underpredicts the power-law exponent for
$r=160$ and 1200, while it underpredicts the power-law exponent for 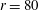 $r=80$ (always predicting
$r=80$ (always predicting 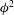 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}^{2}$ behaviour instead of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}^{2}$ behaviour instead of 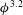 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}^{3.2}$).
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}^{3.2}$).