Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Xu, A.
Shi, L.
and
Zhao, T.S.
2018.
Lattice Boltzmann simulation of shear viscosity of suspensions containing porous particles.
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Vol. 116,
Issue. ,
p.
969.
Gan, Yanbiao
Xu, Aiguo
Zhang, Guangcai
Zhang, Yudong
and
Succi, Sauro
2018.
Discrete Boltzmann trans-scale modeling of high-speed compressible flows.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 97,
Issue. 5,
Xu, A.
Shi, L.
and
Zhao, T.S.
2018.
Thermal effects on the sedimentation behavior of elliptical particles.
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Vol. 126,
Issue. ,
p.
753.
Yu, Yuan
Liu, Haihu
Zhang, Yonghao
and
Liang, Dong
2018.
Color-gradient lattice Boltzmann modeling of immiscible two-phase flows on partially wetting surfaces.
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science,
Vol. 232,
Issue. 3,
p.
416.
Sobhani, S. M. J.
Bazargan, S.
and
Sadeghy, K.
2019.
Sedimentation of an elliptic rigid particle in a yield-stress fluid: A Lattice-Boltzmann simulation.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 8,
Lin, Zhaowu
Hess, Andrew
Yu, Zhaosheng
Cai, Shengqiang
and
Gao, Tong
2019.
A fluid–structure interaction study of soft robotic swimmer using a fictitious domain/active-strain method.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 376,
Issue. ,
p.
1138.
Wang, Yelong
Yu, Zhaosheng
and
Lin, Jianzhong
2019.
Numerical simulations of the motion of ellipsoids in planar Couette flow of Giesekus viscoelastic fluids.
Microfluidics and Nanofluidics,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 7,
Wu, Mingqiu
Peters, Bernhard
Rosemann, Tony
and
Kruggel-Emden, Harald
2020.
A forcing fictitious domain method to simulate fluid-particle interaction of particles with super-quadric shape.
Powder Technology,
Vol. 360,
Issue. ,
p.
264.
Nizkaya, Tatiana V.
Gekova, Anna S.
Harting, Jens
Asmolov, Evgeny S.
and
Vinogradova, Olga I.
2020.
Inertial migration of oblate spheroids in a plane channel.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 11,
Cui, Yuan-feng
Chang, Xiang-ting
and
Huang, Hai-bo
2020.
Experimental study of an ellipsoidal particle in tube Poiseuille flow.
Journal of Hydrodynamics,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 3,
p.
616.
Qin, Jianhua
Dong, Guodan
and
Zhang, Hui
2021.
Control of a sedimenting elliptical particle by electromagnetic forces.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 3,
Férec, Julien
Bertevas, Erwan
Khoo, Boo Cheong
Ausias, Gilles
and
Phan-Thien, Nhan
2021.
Rigid fiber motion in slightly non-Newtonian viscoelastic fluids.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 10,
Hu, Xiao
Lin, Jianzhong
Guo, Yu
and
Ku, Xiaoke
2021.
Inertial focusing of elliptical particles and formation of self-organizing trains in a channel flow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 1,
Yang, LI
Hong, LIANG
and
ZhenHua, XIA
2022.
Effect of neutrally buoyant oblate spheroid's aspect ratio on its equilibrium position in a square duct.
SCIENTIA SINICA Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 10,
p.
104708.
Li, Yang
Xia, Zhenhua
and
Wang, Lian-Ping
2022.
Inertial migration of a neutrally buoyant oblate spheroid in three-dimensional square duct poiseuille flows.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 155,
Issue. ,
p.
104148.
Zhang, Tianlong
Liu, Hangrui
Okano, Kazunori
Tang, Tao
Inoue, Kazuki
Yamazaki, Yoichi
Kamikubo, Hironari
Cain, Amy K.
Tanaka, Yo
Inglis, David W.
Hosokawa, Yoichiroh
Yaxiaer, Yalikun
and
Li, Ming
2022.
Shape-based separation of drug-treated Escherichia coli using viscoelastic microfluidics.
Lab on a Chip,
Vol. 22,
Issue. 15,
p.
2801.
Wang, Wen-Quan
Wang, Jinling
Cui, Guanzhe
Pei, Junxian
and
Yan, Yan
2022.
A numerical study on elliptical particle deposition with an immersed boundary-lattice Boltzmann method.
Computers & Fluids,
Vol. 246,
Issue. ,
p.
105644.
Lin, Pei-Feng
Hu, Xiao
and
Lin, Jian-Zhong
2022.
Inertial focusing and rotating characteristics of elliptical and rectangular particle pairs in channel flow.
Chinese Physics B,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 8,
p.
080501.
Takeishi, Naoki
Yamashita, Hiroshi
Omori, Toshihiro
Yokoyama, Naoto
Wada, Shigeo
and
Sugihara-Seki, Masako
2022.
Inertial migration of red blood cells under a Newtonian fluid in a circular channel.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 952,
Issue. ,
Zhou, Huajie
Chen, Wenbo
Xuan, Chengliang
Qin, Zhangrong
and
Wen, Binghai
2023.
Three-dimensional simulation of red blood cell particle sedimentation.
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science,
Vol. 237,
Issue. 11,
p.
2485.
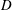 $D$), inertia of the particle and the flow, and the particle geometry (both prolate and oblate ellipsoids) are considered. When a prolate particle with
$D$), inertia of the particle and the flow, and the particle geometry (both prolate and oblate ellipsoids) are considered. When a prolate particle with 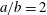 $a/b=2$ is inside a wider tube (e.g.
$a/b=2$ is inside a wider tube (e.g. 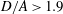 $D/A>1.9$), where
$D/A>1.9$), where 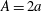 $A=2a$ is the length of the major axis of the particle, the terminal stable state is tumbling. When the prolate particle is inside a narrower tube (
$A=2a$ is the length of the major axis of the particle, the terminal stable state is tumbling. When the prolate particle is inside a narrower tube (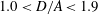 $1.0<D/A<1.9$), log-rolling or kayaking modes may appear. Which mode occurs depends on the competition between fluid and particle inertia. When the fluid inertia is dominant, the log-rolling mode appears, otherwise, the kayaking mode appears. Inclined and spiral modes may appear when
$1.0<D/A<1.9$), log-rolling or kayaking modes may appear. Which mode occurs depends on the competition between fluid and particle inertia. When the fluid inertia is dominant, the log-rolling mode appears, otherwise, the kayaking mode appears. Inclined and spiral modes may appear when 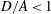 $D/A<1$ and
$D/A<1$ and 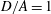 $D/A=1$, respectively. For a prolate ellipsoid with
$D/A=1$, respectively. For a prolate ellipsoid with 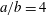 $a/b=4$, if
$a/b=4$, if 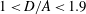 $1<D/A<1.9$, there is only the kayaking mode and the log-rolling mode is not observed. When an oblate particle is inside a wider tube (e.g.
$1<D/A<1.9$, there is only the kayaking mode and the log-rolling mode is not observed. When an oblate particle is inside a wider tube (e.g. 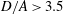 $D/A>3.5$), it may adopt the log-rolling mode. Inclined and intermediate modes are firstly identified in narrower tubes. The phase diagram of the modes is also provided. The modes in the phase diagrams were not found to be affected by the initial state of the particle based on limited observation.
$D/A>3.5$), it may adopt the log-rolling mode. Inclined and intermediate modes are firstly identified in narrower tubes. The phase diagram of the modes is also provided. The modes in the phase diagrams were not found to be affected by the initial state of the particle based on limited observation.


