No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 April 2020
The STAR*D is a pragmatic clinical trial that showed lower remission rate and higher relapse rate when more strategies were used.[1]
Assess clinical improvement in symptoms related to depression, anxiety and sleep, based on the number of strategies used.
Descriptive, non-interventional, prospective study including outpatients diagnosed with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) with sub-optimal response to standard antidepressants. In those patients a change on the therapeutic strategy (switch of antidepressant, combination of antidepressants, augmentation or a combination of previous strategies) had to be considered necessary. Follow-up period was 22–26 weeks.
364 patients were included by 58 psychiatrists, 336 were analyzed (92.3%) and 315 (86.5%) completed the follow-up.
[Difference last visit vs. basal]
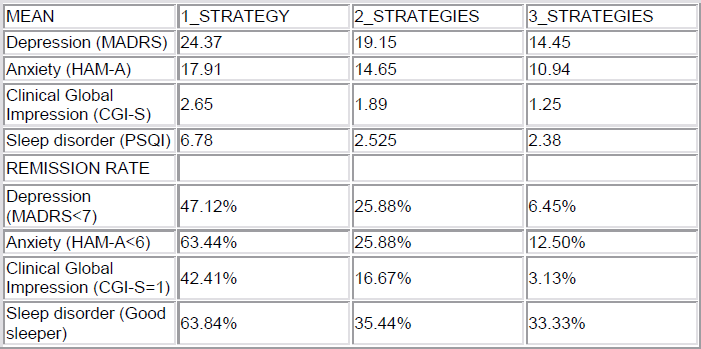
p < 0.0001 in all measures
The more changes on strategies used the less improvement on clinical symptoms and remission rates.
This study has been sponsored by AstraZeneca Farmaceutica Spain, SA.
Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.