No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 August 2021
Several studies demonstrate that disgust, defined as a revulsion response aimed at distancing an individual from a potentially harmful or noxious stimulus, is linked to post-traumatic stress following sexual trauma even when accounting for associated fear and anxiety. One of the suggested mechanisms implicated in this association is a feeling of mental contamination. Recent neuroimaging studies demonstrated that exposure to contamination activates the insular cortex. In addition, disgust sensitivity correlates with the activation of the insular cortex.
We aimed to investigate the psychopathological role of the emotion of disgust in the developement of anxiety symptoms in patient with an history of abuse.
We enrolled 84 patients admitted in Psychiatric Unit of Careggi with diagnosis of Anxiety Disorders. We administered to them: Zung Anxiety Scale (ZSAS), Childhood Trauma Questionnaire (CTQ), Disgust Propensity and Sensitivity Scale-revised (DPSS-r).
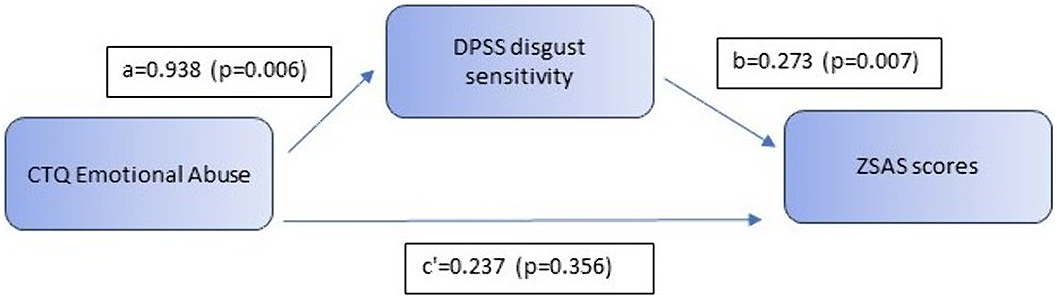 Results showed a significant mediation of the association between CTQ emotional abuse scores and total ZSAS scores via DPSS disgust sensitivity scores in patients with anxiety disorders (p=0.022). Total effect and indirect effect of emotional abuse on severity of anxiety symptoms were significant (total effect = 0.494; p=0.051, indirect effect: 0.256, p=0.022), while there was no significant direct effect from emotional abuse to anxiety symptoms in the total model (direct effect: 0.237, p=0.356). The model explained 18% of variance in anxiety symptomatology (R2=0.18).
Results showed a significant mediation of the association between CTQ emotional abuse scores and total ZSAS scores via DPSS disgust sensitivity scores in patients with anxiety disorders (p=0.022). Total effect and indirect effect of emotional abuse on severity of anxiety symptoms were significant (total effect = 0.494; p=0.051, indirect effect: 0.256, p=0.022), while there was no significant direct effect from emotional abuse to anxiety symptoms in the total model (direct effect: 0.237, p=0.356). The model explained 18% of variance in anxiety symptomatology (R2=0.18).
Such preliminary data suggest a possible mediating role of disgust in development and maintenance of childhood abuse-related anxiety, making it a potential target for psychotherapy.
No significant relationships.
Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.