No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Contrimetric: Article Citation Contribution Indicator for paper impact evaluation
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 October 2023
Abstract
The Journal Impact Factor (JIF), generated by Eugene Garfield in 1964, is a well-known and widely accepted indicator for evaluating journal influence when scholar submit their papers to different periodicals. Different paper has its own citation performance after published online. Thus, the JIF is always changing in each year when times updates. This paper introduces a newly designed bibliometric indicator, Article Citation Contribution Indicator (ACCI), named as Contrimetric (from Contribution Metric). The indicator meets the criteria as it has special characteristics, such as easy to understand, open, innovating, and applicable to different publications. Based on the Journal Impact Factor (JIF), the ACCI is a new indicator that measures the impact of individual papers within a specific journal. Treating a journal as an independent scientific community, each paper can be viewed as a community member, with ACCI>0 indicating that the paper’s academic impact has a greater impact than the community average, while ACCI<0 indicates that the paper’s academic findings, innovations, spreading and impact are below the community average. The ACCI ranges theoretically in [-1, infinity], with ACCI=-1 for papers with zero citations after publication.
For purpose of exploring the positive (or negative) effects of an author’s single article on the improvement of journal impact factor, we proposed the ACCI. It is defined as a specific value to calculate the contribution of a single paper to its discipline or journal, its equation is shown as below:(1)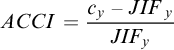
It can be calculated that the value of ACCI is -1 when the paper has 0 citation. The value range of ACCI is theoretically in [-1,+∞). When ACCI∈[-1,0), it indicates that the article has a lower value than the average citation level or has brought negative effect on JIF; and when ACCI∈(0,+∞), it indicates that the article citations is higher than average level and has brought a positive contribution in terms of citations. Furthermore, its innovation, new discoveries contribute higher level than other papers. Hereafter, we might treat each journal as a specific scientific community in its field.
Let’s have an example to compute any article. We retrieved the article as below: Abdelmageed, S. and T. Zayed, A study of literature in modular integrated construction - Critical review and future directions. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020. 277. DOI:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124044. The article was published in 2020, and the total cites received in 2021 and 2022 was 13 and 24. The 2021 and 2022 Impact Factor of Journal of Cleaner Production were both 11.1, thus ACCI-1(Contributing Factor) = (13-11.1)/11.1 = +0.17, ACCI-2(Contributing Factor) = (24-11.1)/11.1 = +1.16. This paper had brought positive effect on the JIF. This paper had been higher citations in influence than others.
The ACCI is an important index for scholars to carry out research and academic journal editors to select proper papers. For authors, who can use ACCI to categorize articles from a particular journal or in a particular year, the articles that ACCI>0 would fell into positive group, then use other bibliometric tools to mine the specific scientific view. And for academic journal editors, the author’s citing performance can be reflected by their ACCI report. Therefore, the bibliometric index-Article Citation Contribution Indicator (ACCI) is a new article evaluation tool in bibliometrics. Each paper published in journal with JIF will have two ACCI index values, CF-1 and CF-2. The information behind CF index will bring us different analysis. It is also an indicator for university subjects evaluation, scientific research management and academic contribution measurement in some field, which is an important index reflecting the academic level of a certain discipline. The Contrimetric can be statistically used to classify articles for finding important papers and is an innovative member of the metrics family.
- Type
- Abstracts
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2023. Published by Cambridge University Press


