No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Delayed Neurological Deterioration in ICH Due to Cerebral Infarction
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 December 2014
Abstract
An abstract is not available for this content so a preview has been provided. As you have access to this content, a full PDF is available via the ‘Save PDF’ action button.
- Type
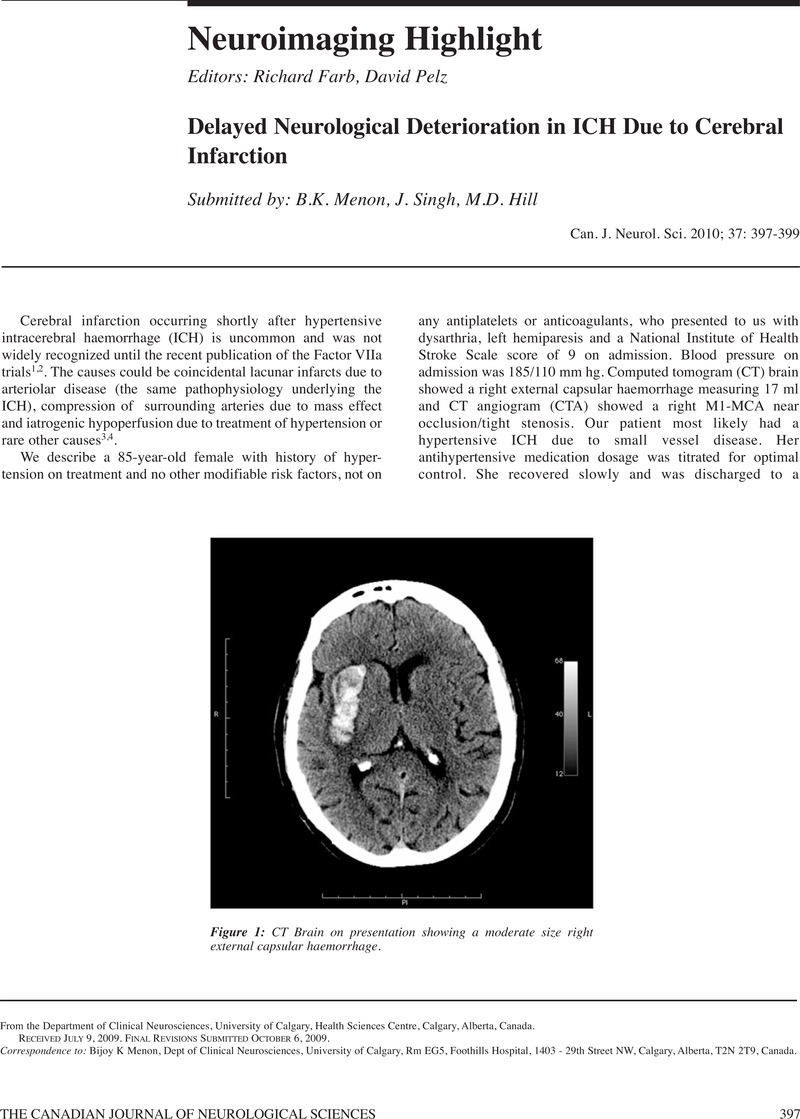
- Neuroimaging Highlight
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Canadian Journal of Neurological 2010
References
1.
Mayer, SA, Brun, NC, Begtrup, K, Broderick, J, Davis, S, Diringer, MN, et al.
Recombinant activated factor VII for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med.
2005 Feb 24;352(8): 777–85.Google Scholar
2.
Mayer, SA, Brun, NC, Begtrup, K, Broderick, J, Davis, S, Diringer, MN, et al.
Efficacy and safety of recombinant activated factor VII for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med.
2008 May 15; 358(20):2127–37.Google Scholar
3.
Kim, CH, Kim, JS.
Development of cerebral infarction shortly after Intracerebral haemorrhage. Eur Neurol. 2007;57:145–9.Google Scholar
4.
Sinar, EJ, Mendelow, AD, Graham, DI, Teasdale, GM.
Experimental Intracerebral haemorrhage: effects of a temporary mass lesion. J Neurosurg. 1987;66:568–76.Google Scholar
5.
Rincon, F, Mayer, SA.
Novel therapies for intracerebral hemorrhage. Curr Opin Crit Care.
2004 Apr;10(2):94–100.Google Scholar
6.
Zazulia, AR, Diringer, MN, Derdeyn, CP, Powers, WJ.
Progression of mass effect after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke.
1999;Jun;30(6):1167–73.Google Scholar
7.
Inaji, M, Tomita, H, Tone, O, Tamaki, M, Suzuki, R, Ohno, K.
Chronological changes of perihematomal edema of human intracerebral hematoma. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2003;86:445–8.Google Scholar


