Book contents
- Frontmatter
- Contents
- List of contributors
- Preface
- 1 The normal child: growth and development of the infant and child; frequent and important normal variants
- 2 Neonatal imaging
- 3 Congenital cardiac malformations
- 4 Pediatric trauma
- 5 Nontraumatic pediatric emergencies
- 6 Infections, inflammations and HIV
- 7 Pediatric tumors
- 8 Ischemia in children
- 9 Metabolic bone disorders
- 10 Skeletal dysplasias and syndromes
- 11 Transplant imaging in children
- 12 Iatrogenic devices
- 13 Radiation protection in children undergoing medical imaging
- Index
- References
4 - Pediatric trauma
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 December 2010
- Frontmatter
- Contents
- List of contributors
- Preface
- 1 The normal child: growth and development of the infant and child; frequent and important normal variants
- 2 Neonatal imaging
- 3 Congenital cardiac malformations
- 4 Pediatric trauma
- 5 Nontraumatic pediatric emergencies
- 6 Infections, inflammations and HIV
- 7 Pediatric tumors
- 8 Ischemia in children
- 9 Metabolic bone disorders
- 10 Skeletal dysplasias and syndromes
- 11 Transplant imaging in children
- 12 Iatrogenic devices
- 13 Radiation protection in children undergoing medical imaging
- Index
- References
Summary
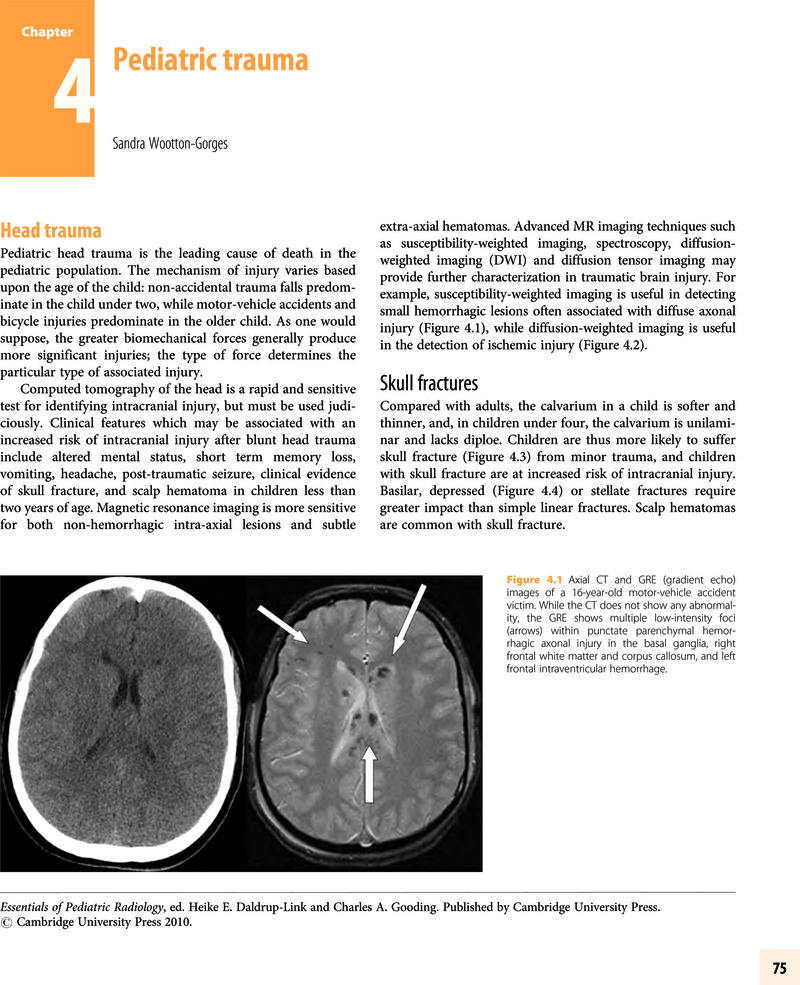
- Type
- Chapter
- Information
- Essentials of Pediatric RadiologyA Multimodality Approach, pp. 75 - 97Publisher: Cambridge University PressPrint publication year: 2010
References
- 1
- Cited by