Article contents
A pathway to compound semiconductor additive manufacturing
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 August 2019
Abstract
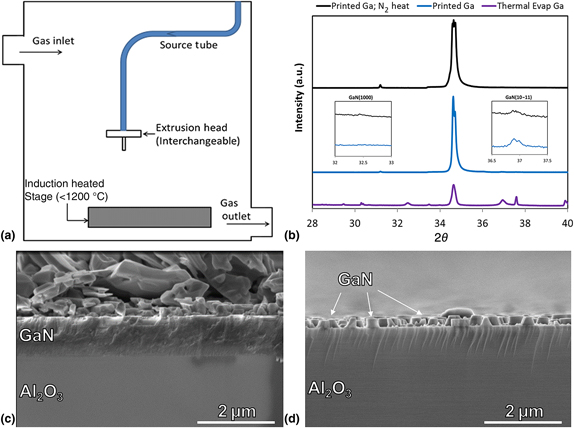
The rise of additive manufacturing (AM) has enabled the rapid production of complex part geometries across multiple material domains. To date, however, AM of inorganic semiconductor materials has not been fully realized due to the difficulty of forming single-crystal materials with traditional AM processes. Here, we demonstrate a novel semiconductor synthesis method using a combination of liquid and gas precursors to additively print gallium nitride. Growth rates of 1–2 µm/min are demonstrated in printed regions while maintaining epitaxial alignment with the substrate. We also outline critical variables for the future development, improvement, and implementation of the proposed process.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s) 2019
References
- 4
- Cited by


