Article contents
Anisotropic thermal conductivity in direction-specific black phosphorus nanoflakes
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 September 2019
Abstract
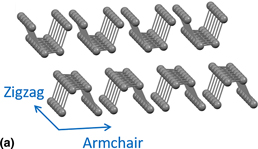
Herein, the authors report our pioneering demonstration of the anisotropic thermal properties of black phosphorus (BP) nanoflakes. The nanoflakes were produced using a scotch tape-based mechanical exfoliation technique. Their thickness was characterized using Atomic Force Microscopy The anisotropic direction of the nanoflakes was determined by the Raman Spectroscopy equipped with a polarized laser. Then, a temperature-dependent Raman spectroscopy method was utilized to study the thermal transport properties of the BP nanoflakes. The results indicated that the thermal conductivities of zigzag BP and armchair nanoflakes are 30.6 and 12.6 W/m·K, respectively. This fundamental thermal study gives insight into the future fabrication of nanoscale electronic devices with thermal properties that can be well controlled.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s) 2019
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally to this work.
References
- 6
- Cited by



